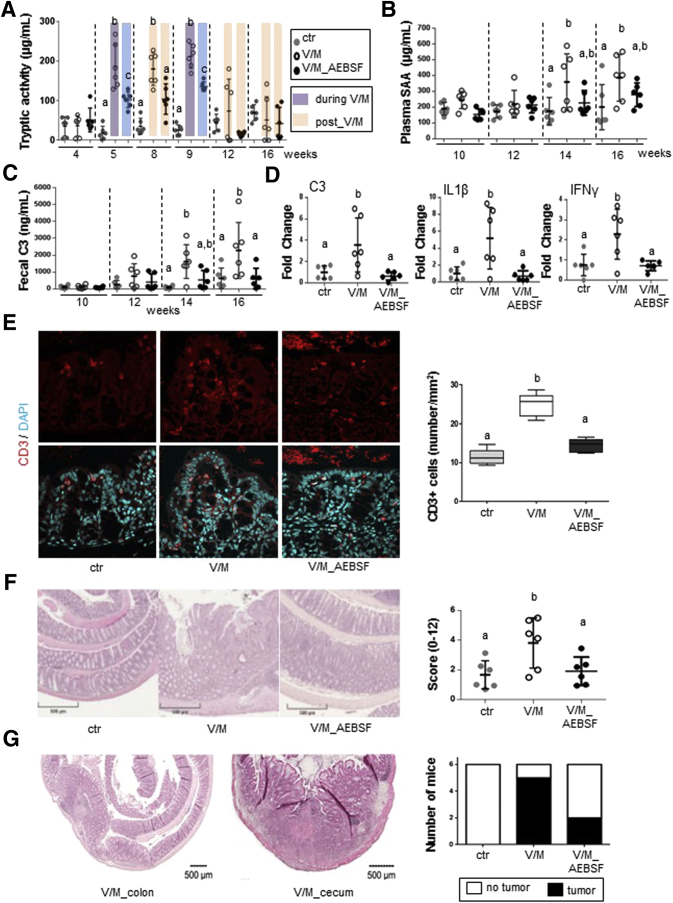
Figure 7.
Excessive large intestinal PA accelerates colitis development in IL10-/-mice. (A) Kinetic of the fecal serine protease activity in IL10-/- mice. (B, C) Development of plasma serum amyloid A levels (systemic inflammation marker) and fecal complement component 3 (C3) levels (marker for intestinal inflammation) in IL10-/- mice. (D) mRNA expression levels of C3, IL1β, and interferon-γ in large intestinal tissue of IL10-/- mice. (E) T-cell infiltration in the proximal colon was determined by immunofluorescence staining of CD3+ cells. Quantification of CD3+ T cells per mm2 at 6 representative regions in tissue sections per mouse. (F) The left panel shows representative pictures of hematoxylin-eosin-stained colonic tissue and the right panel shows the histopathologic score of individual IL10-/- mice. (G) The left panel shows representative pictures of hematoxylin-eosin-stained tumors that were exclusively observed in the cecum and colon of V/M-treated IL10-/- mice. The right panel shows the prevalence of tumor formation in the respective treatment group. IFN, interferon; SAA, serum amyloid A.