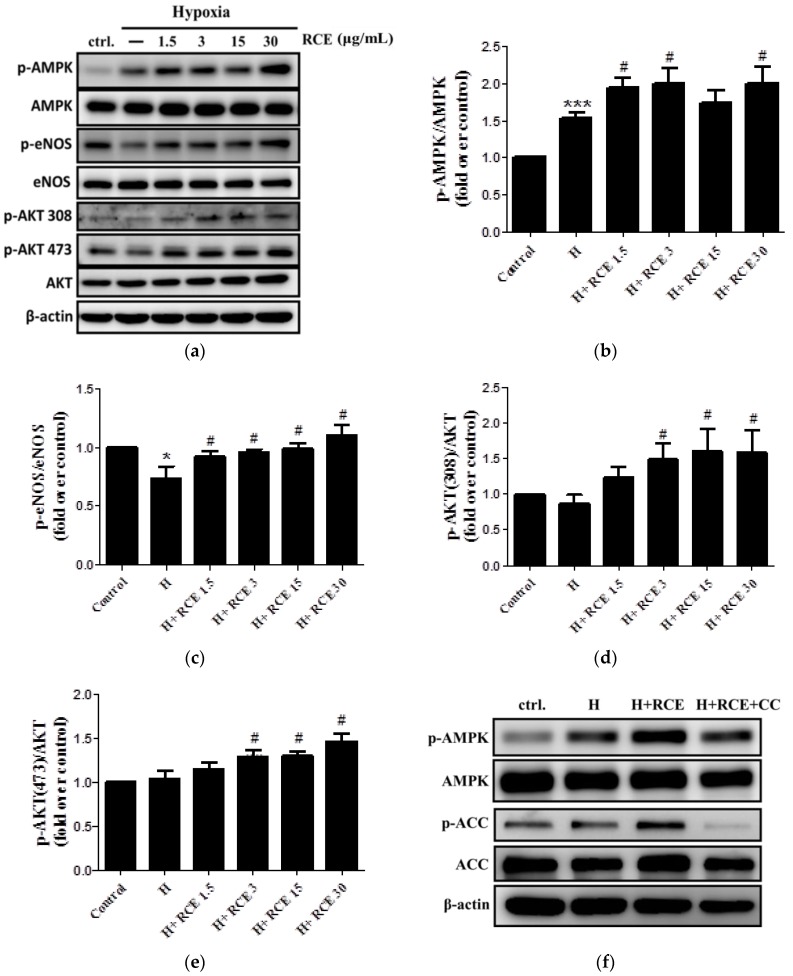
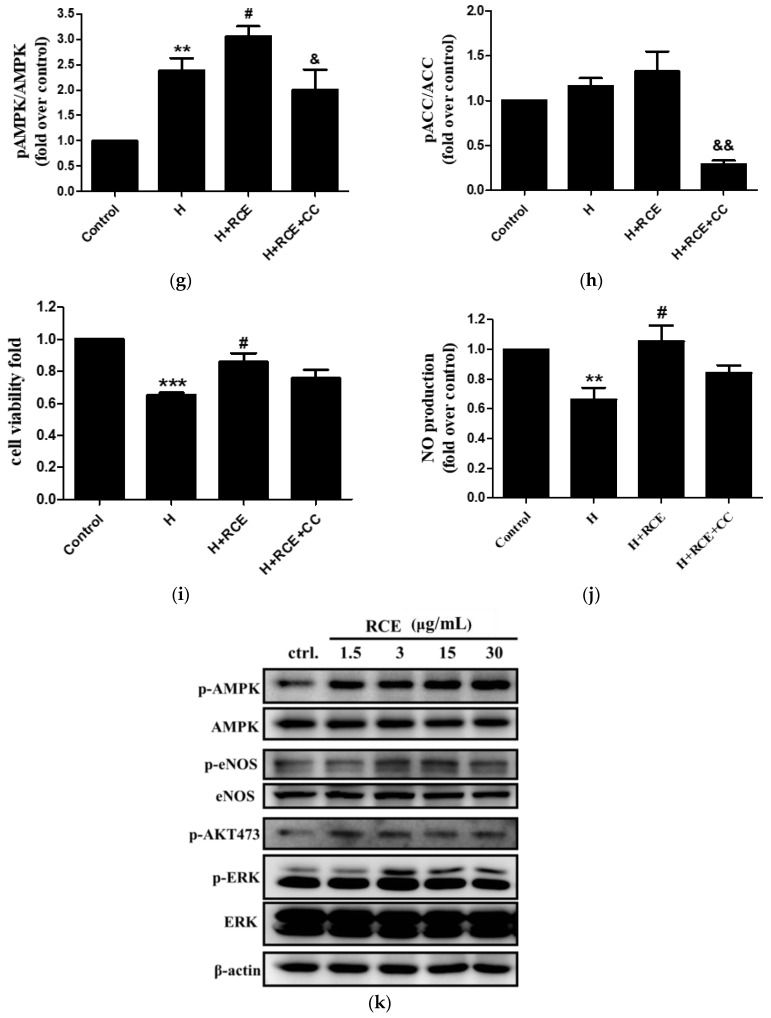
Figure 4.
Effect of Rhodiola crenulata root extract on the AMP-activated kinase-AKT-endothelial nitric oxide synthase (AMPK-AKT-eNOS) axis in HUVECs under hypoxic conditions. Phosphorylation of AMPK (Thr172), eNOS (Ser1177), and AKT (Thr308 and Thr473) was analyzed by Western blotting (a). Quantitative analysis of the relative levels of p-AMPK (b), p-eNOS (c), p-AKT (Thr308; (d)), and p-AKT (Thr473; (e)) was conducted. The cells were further treated with AMPK inhibitor (CC; compound C; 2 μM) for 30 min before RCE treatment (3 μg/mL) and hypoxia exposure (1% O2) for 24 h. The effects of CC on p-AMPK and p-ACC were analyzed by Western blotting (f) and quantified ((p-AMPK; (g)) and (p-acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase (ACC); (h)). β-actin served as a loading control. Cell viability was measured by using a CCK-8 kit (i), and the supernatant was collected for Griess assay (j). The cells were treated with RCE under normoxia (k). Results represent the mean ± SEM (n = 6). * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001 versus control; # p < 0.05 versus hypoxia; & p < 0.05 and && p < 0.01 versus hypoxic condition with RCE.