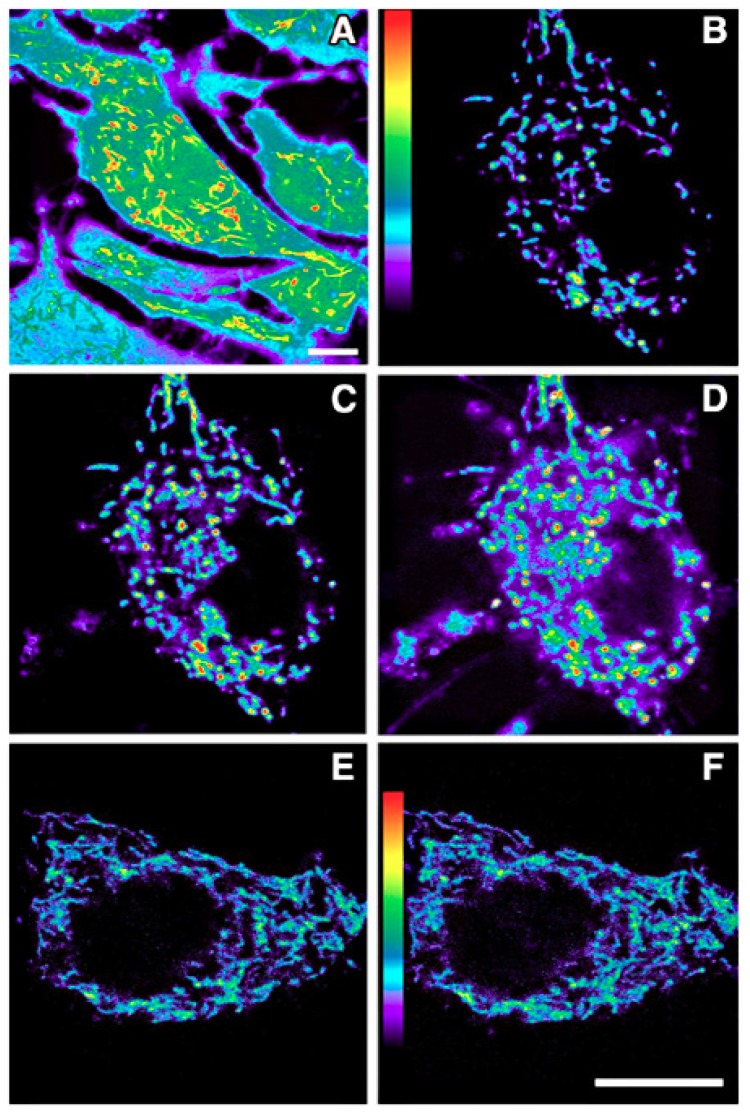
Figure 4.
Fluorescent imaging of the intense generation of reactive oxygen species in a cultured astrocyte at 5 min (C) and 10 min (D) after its exposure to an oxidizing agent (H2O2). The cell shown in panels (E) (5 min) and (F) (10 min) was also exposed to the H2O2, but additionally, melatonin was present in the culture medium. Clearly, melatonin was taken into the cell and into mitochondria where it reduced reactive oxygen species generation or quickly scavenged them when they were produced. Dihydrorhodamine 123 was used to visualize free radical generation. (A) is an enhanced pseudocolor image which shows the higher levels of reactive oxygen species in mitochondria relative to other organelles. (B) is the astrocyte (also shown in the panels (C,D)) before its exposure to H2O2. Figure provided by Mei-Jie Jou. Scale bar = 1 µm.