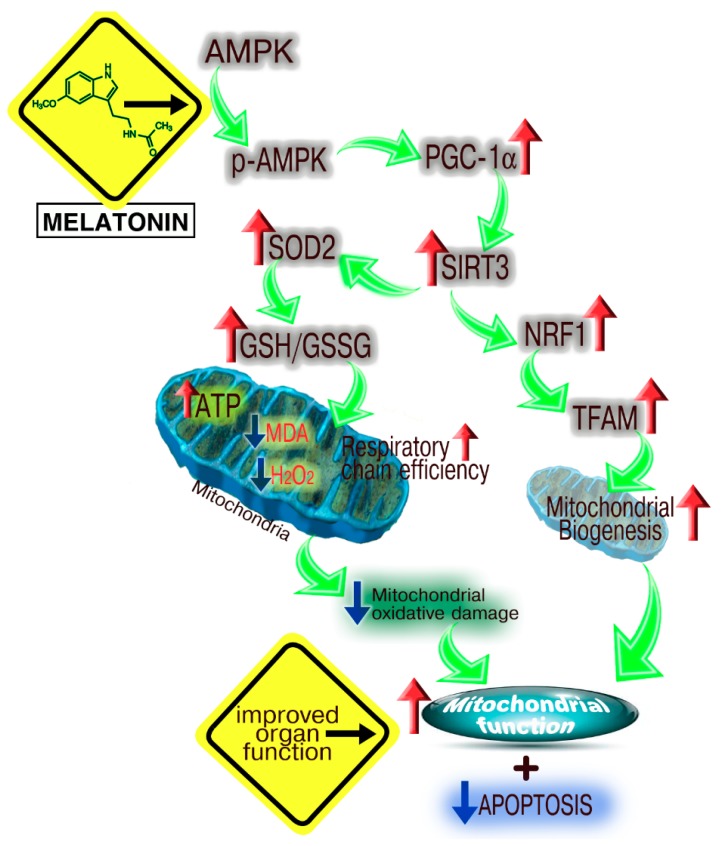
Figure 8.
A summary of the proposed mechanisms by which melatonin preserves myocardial cell function after ischemia/reperfusion injury in type 1 diabetic rats. The involvement of AMPK→pAMPK was shown using compound C, a specific blocker of AMPK-signaling. The role of SIRT3 was documented with the use of SIRT3 siRNA. Melatonin protects against myocardial damage due to ischemia/reperfusion as indicated. Figure drawn from the findings of Yu et al. [216]. Red arrows indicate stimulation; blue arrows indicate inhibition; green arrows indicate flow of information.