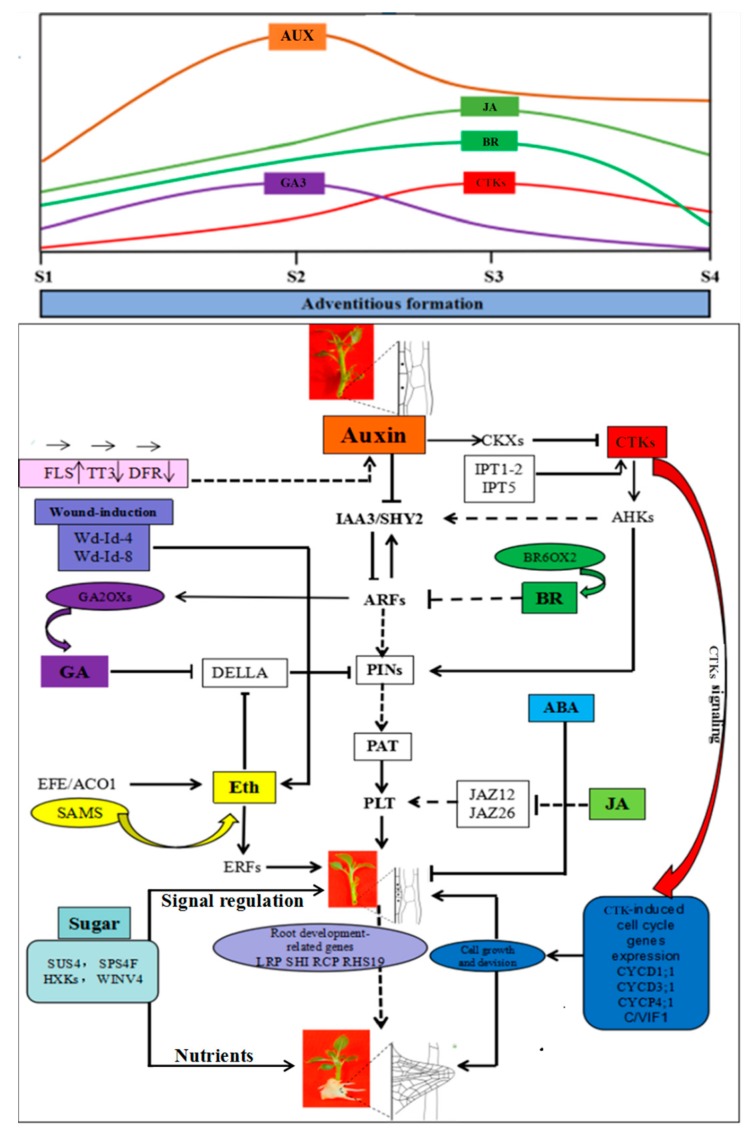
Figure 10.
Hypothetical model for the regulation of adventitious root formation in stem cuttings of ‘T337’ apple rootstocks by hormones and sugar signaling crosstalk. AUX, Auxin; CTKs: Cytokinins; GA, Gibberellic acid; BR, Brassinolide; JA, Jasmonic acid; ABA, Abscisic acid; Eth, Ethylene; FLS, Flavonol synthase; TT3, DRF, Dihydroflavonol 4-reductase; IAA3/SHY2, AUX/IAA transcriptional regulator family protein; PINs, Auxin efflux carrier family proteins; PAT, auxin polar transport-related gene; PLT, Integrase-type DNA-binding superfamily protein gene; IPT1-2, Isopentenyl adenosine transferase gene 1-2; IPT5, Isopentenyl adenosine transferase gene 5; AHK, histidine kinases; CKXs, Cytokinin oxidases; BR6OX2, Brassinosteroid-6-oxidase 2; JAZ12, Jasmonate-zim-domain protein 12; JAZ26, Jasmonate-zim-domain protein 26; Wd-Id-4, Wound responsive family gene 4; Wd-Id-8, Wound responsive family gene 8; GA2OXs, Gibberellin 2-oxidases; DELLA, Gibberellic acid insensitive; EFE/ACO1, Ethylene forming enzyme; SAMS, S-adenosylmethionine synthetase; ERF, Ethylene response factor; SUS4, sucrose synthase 4; SPS4F, Sucrose-phosphate synthase family protein; HXKs, Hexokinases; WINV4, cell wall invertase 4; LRP, Lateral root primordium (LRP) protein-related; SHI, Lateral root primordium (LRP) protein-related; RCP, Root cap-related; CYCD1;1, CYCD3;1, CYCP4;1, Cell cycle-related genes; C/VIF1, Cell wall/vacuolar inhibitor of fructosidase 1. Different colored arrows indicate different types of hormone-related genes regulate AR formation in apple rootstock.