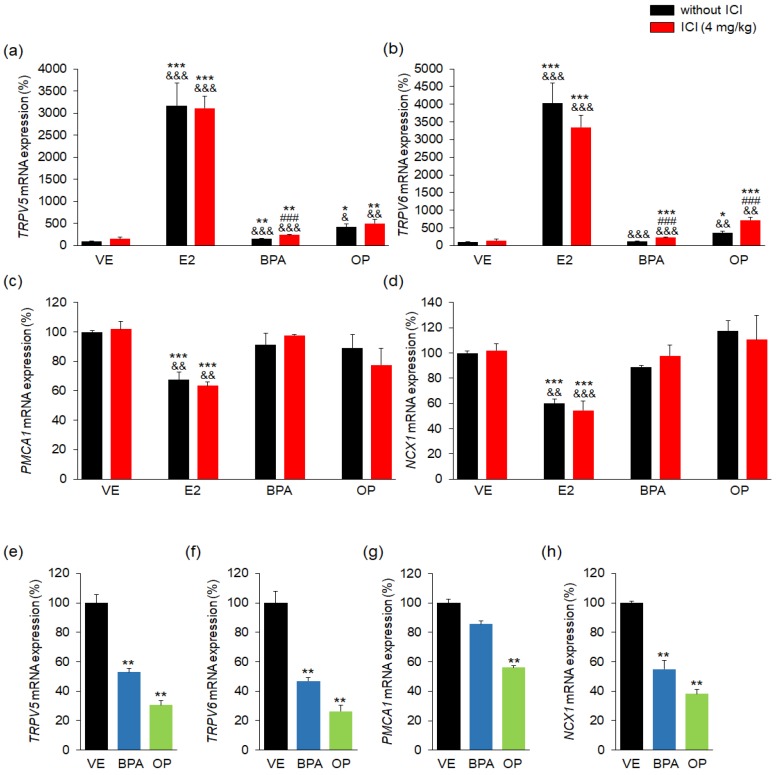
Figure 2.
E2, BPA, and OP change the expressions of TRPV6, TRPV5, PMCA1, and NCX1 in maternal uterus and implantation sites. Mice were sacrificed at GD 4.5 (24 h after final injection) to collect uterus tissues and at GD 5.5 (after 48 h after final injection) to collect implantation sites. The mRNA expressions of calcium transporter channel genes in uterus and implantation sites were assessed. The mRNA levels of TRPV6, TRPV5, PMCA1, and NCX1 genes were measured by using real-time PCR and were normalized to that of 18S ribosomal RNA (RN18S). In uterus, (a) the expressions of TRPV5 mRNA were significantly high in the E2, E2 + ICI, BPA + ICI, OP, and OP + ICI groups; (b) TRPV6 mRNA level changes were similar to those for TRPV5 expression. mRNA expression of TRPV5 and TRPV6 in uteri were higher in BPA + ICI group than in the BPA group; (c,d) mRNA level of PMCA1 and NCX1 were significantly decreased by E2 and E2 + ICI. In implantation sites; (e–h) the mRNA levels of TRPV6, TRPV5, PMCA1, and NCX1, respectively, were markedly low in all groups. Statistical significance was determined by two-way ANOVA. * p < 0.05 vs. VE, ** p < 0.01 vs. VE, *** p < 0.001 vs. VE, ### p < 0.001 EDs + ICI vs. EDs, & p < 0.05 vs. ICI, && p < 0.01 vs. ICI, &&& p < 0.001 vs. ICI. n = 5 mice per group for uterus, n = 3 mice per group for implantation sites. Treatments: E2; 40 µg/kg/day, BPA; 100 mg/kg, OP; 100 mg/kg, ICI; 4 mg/kg.