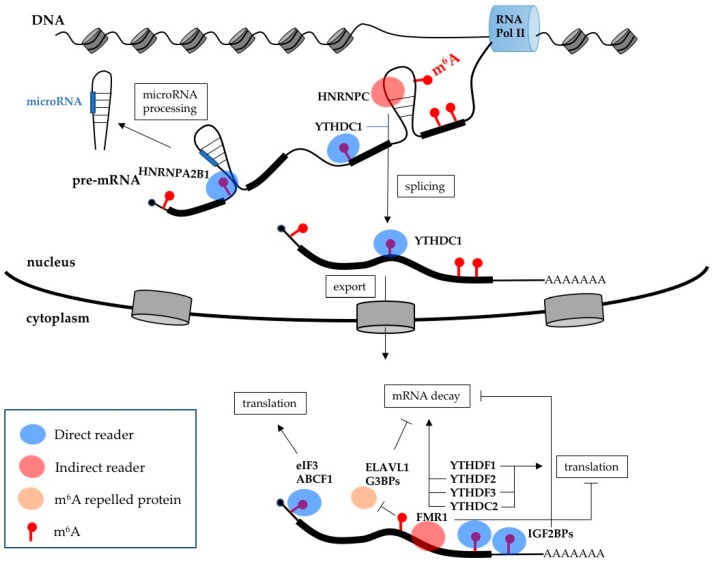
Figure 2.
Functional roles of m6A modification on mRNA expression. Most of m6A’s effects on mRNA metabolism are mediated by reader proteins whose binding can be directly or indirectly affected by m6A. In the nucleus, the direct readers are YTHDC1 and HNRNPA2, which stimulate splicing and microRNA processing, respectively. YTHDC1 also stimulates mRNA export. The splicing regulator HNRNPC (heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein) is an indirect reader whose binding is favored by structural rearrangement induced by m6A modification. In the cytoplasm, mRNA translation is stimulated by the direct reader eIF3, ABCF1 (ATP binding cassette subfamily F member 1), YTHDF1, YTHDF3 and YTHDC2, while it is inhibited by the indirect reader FMR1. mRNA decay is increased by the direct readers YTHDF2, YTHDF3 and YTHDC2, while it is inhibited by the direct readers IGF2BPs (insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein) and the m6A-repelled proteins ELAVL1 (ELAV like RNA binding protein 1) and G3BPs (G3BP stress granule assembly factor).