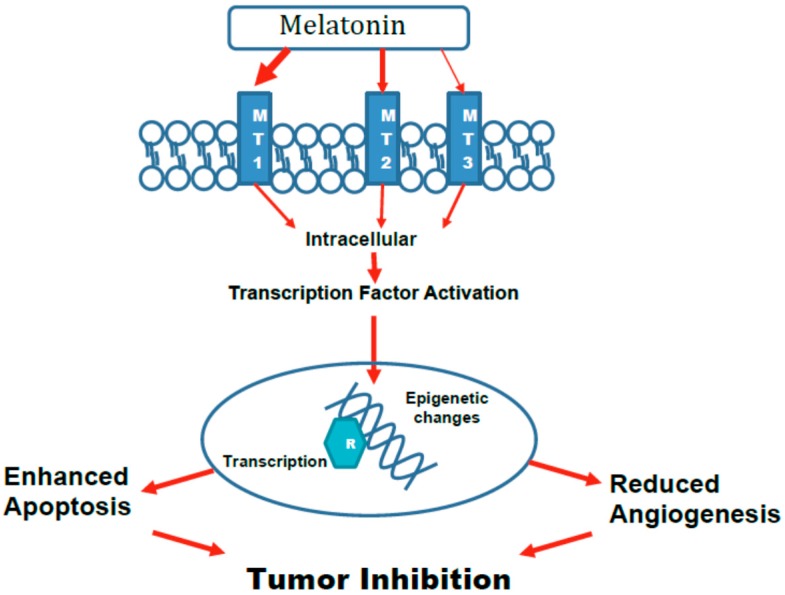
Figure 1.
The effects of melatonin on carcinogenesis that directly Inhibit tumors. Melatonin interacts with its surface receptors to activate intracellular signaling cascades. The size of the arrows reflects the importance of the receptor subtype. Intracellular signaling leads to activation of transcription factors that cause changes to the DNA in a manner that enhance apoptosis of cancer/pre-cancer cells and reduce angiogenesis which is necessary for tumor growth and metastasis.