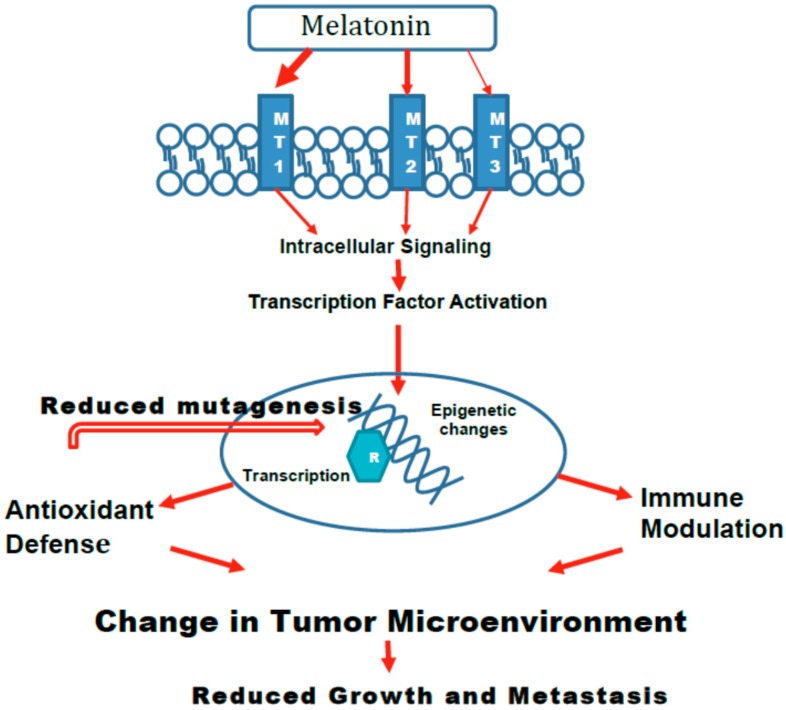
Figure 2.
The effects of melatonin on carcinogenesis that Indirectly Inhibit tumors. The initial steps in the indirect action of melatonin on suppressing tumors are the same as Figure 1. Melatonin interacts primarily with MT1 receptors to activate intracellular signaling that leads to activation of transcription factors. The subsequent changes to the DNA provide up-regulation of antioxidant defenses that can reduce mutations that lead to initiation of cancer. Furthermore, the up-regulation of antioxidants and modifications to immune responses alter the microenvironment of cancer cells in a manner that reduces cancer progression and metastasis.