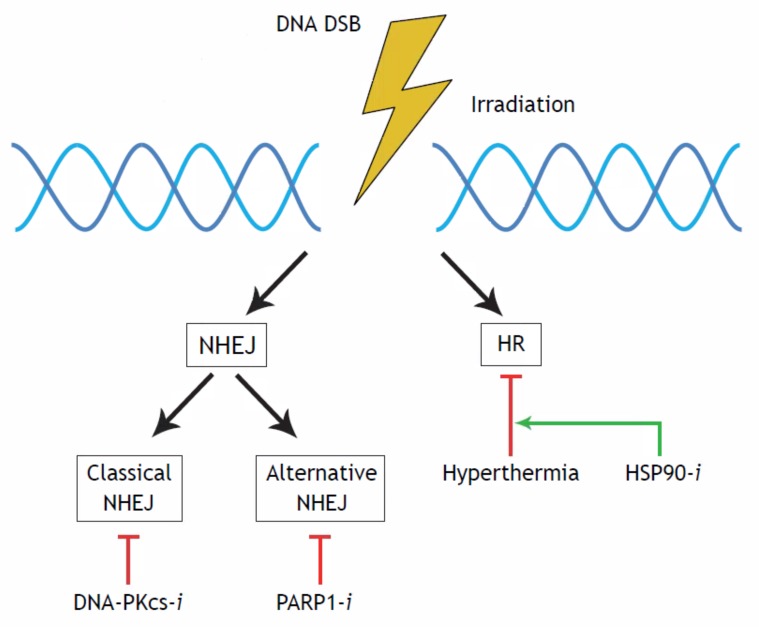
Figure 1.
Schematic overview of DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair processes. Treatment options are shown underneath the pathway they act upon. A DSB can be repaired via two major pathways, the Non-Homologous End Joining (NHEJ) or the Homologous Recombination (HR). The NHEJ can be divided into two sub-pathways, the Classical NHEJ (cNEHJ) and the Alternative NHEJ (AltNEHJ). Each pathway can be blocked by specific inhibitors. A DNA-PKcs-i can disrupt the Classical NHEJ, A PARP1-i the Alternative NHEJ and Hyperthermia can temprarily inactive the HR. A HSP90-i can enhance the effectiveness of HT.