Table 1.
Factors and pathways that affect MSC migration during bone formation.
| Factor | Ossification Pattern | Pathway | Efficacy | In Vitro or In Vivo | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMPs | Endochondral | Activate SMADs receptor to | MSC condensation 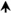
|
In vitro | [21] |
| transduce signals | Recruitment of osteoblast 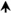
|
||||
| Hoxa13 and | Endochondral | Promote cell-cell adhesion | MSC condensation 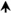
|
In vitro | [22] |
| Hoxd13 | Bone formation 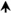
|
||||
| ECM | Endochondral | Self-assembling of MSCs | MSC condensation 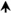
|
In vitro | [23] |
| LL-37 | Intramembranous | MAPK pathway | Expression of EGR1 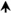
|
In vitro and in vivo | [24] |
| Activation of MAPKs | |||||
| PDGFs | Intramembranous | BMP-Smad1/5/8-Twist1/Atf4 axis | Cell migration 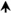
|
In vitro | [25] |
| TGF-β1 | Intramembranous | SMAD signaling | Cell migration 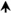
|
In vitro and in vivo | [26] |
| MMP | Intramembranous | Penetrate blood vessel basement membranes | Induce MSC migration | In vitro and in vivo | [27,28] |
| NF-κB ligand | Intramembranous | Activating phosphorylation of ERK, MAPK, Akt, and NF-κB | Cell migration 
|
In vitro | [33] |
| TNFα | Fracture healing | Induce LRG1 secretion | MSC recruitment 
|
In vitro and in vivo | [40] |
| CXCL7 | Fracture healing | Binding CXCR2 | MSC recruitment 
|
In vitro | [36] |
| SDF-1 | Fracture healing | Binding CXCR4 | Osteoblast migration 
|
In vitro and in vivo | [41] |
MSC recruitment 
|
 : Up-regulation.
: Up-regulation.
