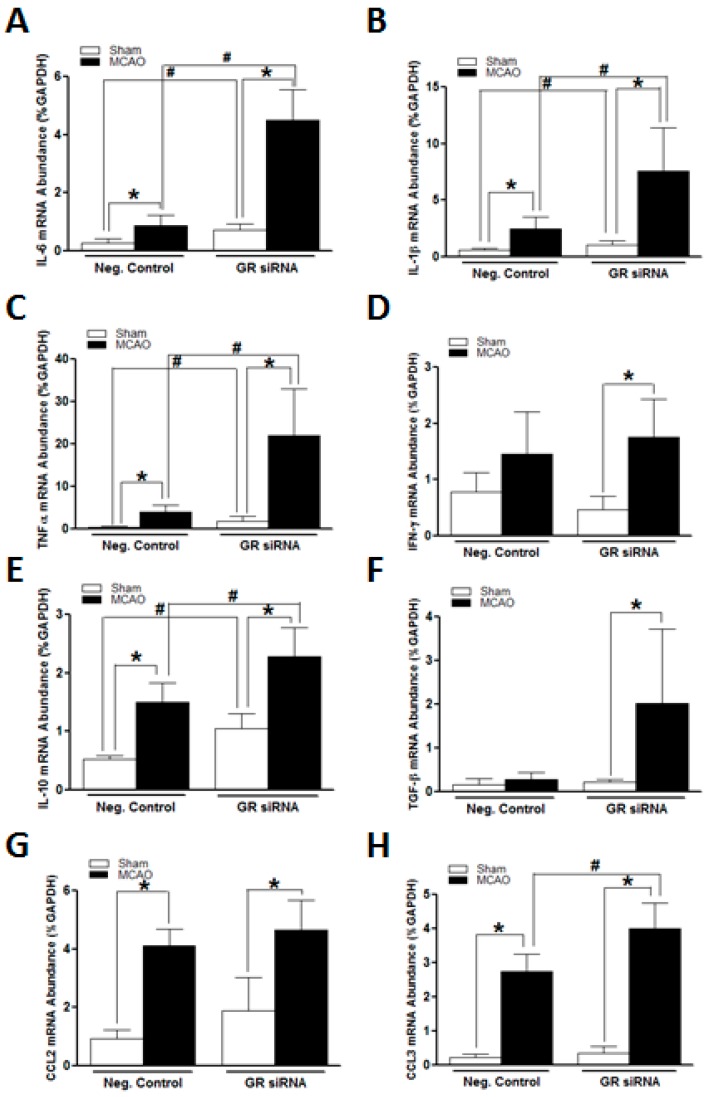
Figure 3.
The GR repression induced heightened inflammatory responses in mice brains following MCAO. The mice received either GR siRNA (100 pmol) or its negative control (Neg. Control; 100 pmol) via intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) injection. A middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) was performed 48 h after i.c.v. injection. Sham animals were subjected to left internal carotid artery exposure but without suture insertion. The brain samples were collected at 12 h after MCAO induction. A quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) was utilized to assess inflammation-related genes expression profiles, including IL-6 (A), LI-1β (B), TNF-α (C), IFN-γ (D), IL-10 (E), TGF-β (F), CCL2 (G) and CCL3 (H), respectively. n = 5. * p < 0.05, MCAO vs. sham; # p < 0.05, GR siRNA vs. Neg. Control.