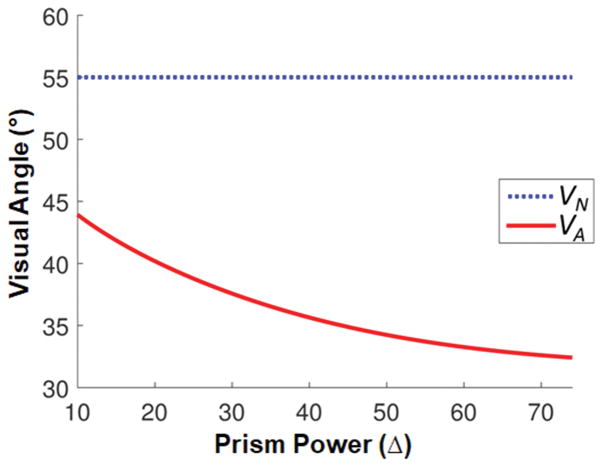
Figure 6.
The angular direction of the apex of the multiplexing prism (MxP) segment (VA) that avoids both monocular diplopia and apical scotoma (red solid line). When the base end of see-through view (the end of the nasal field, VN) is fixed at 55° (blue dotted line) and the tilt angle maximizes field of view (FoV) (Fig. 4), VA for higher power MxPs extend more centrally than lower power MxPs. The optimal visual angular width of the MxP as a function of prism power is the distance between the two curves.