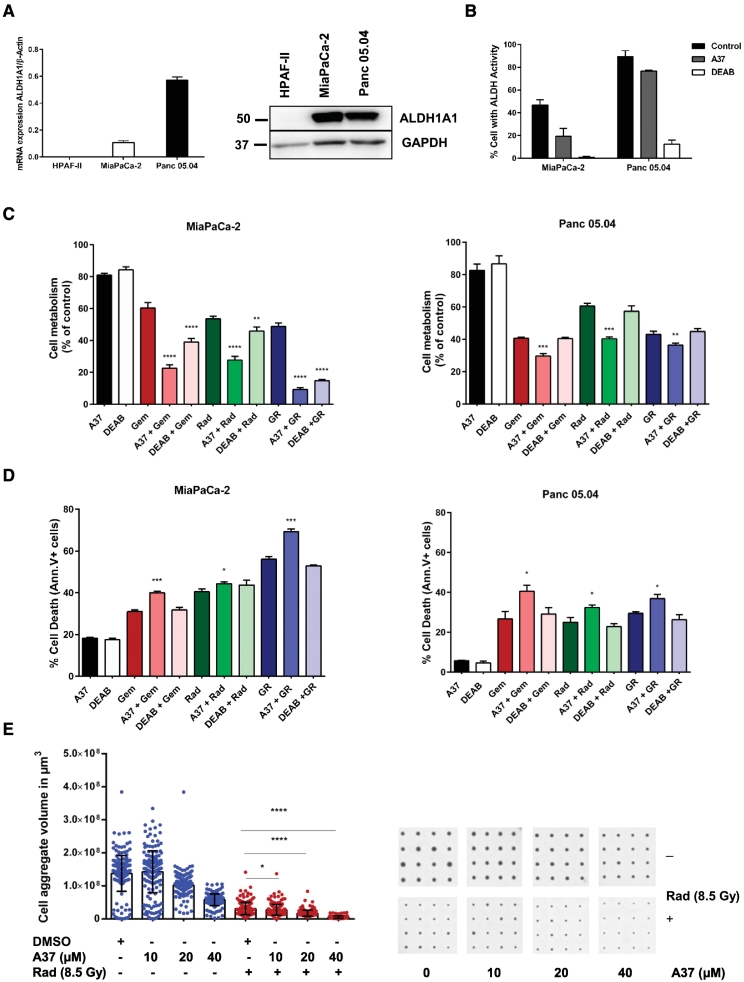
Figure 4.
Inhibition of ALDH1A1 activity reduces cell viability and sensitizes PDAC cells to chemoradiation treatment. (A) Relative mRNA and protein expression of ALDH1A1 in PDAC cells HPAF-II, MiaPaCa-2, and Panc 05.04 cells. (B) Flow cytometry measurement of ALDH1A1 activity in MiaPaCa-2 and Panc 05.04 cells following treatment with ALDH1A1 inhibitors. DEAB treated cells served as negative controls and were used to set the FACS gate. (C) Inhibition of ALDH1A1 for 48 hours using A37 and DEAB (EC20 values) followed by gemcitabine (1 μM for MiaPaCa-2 and 0.25 μM for Panc 05.04), radiation (10 Gy), and chemoradiation for a further 72 hours reduced cell viability. Cell viability was confirmed using MTT assay. (D) Inhibition of ALDH1A1 for 48 hours using A37 and DEAB (EC20 values) followed by gemcitabine, radiation, and chemoradiation augmented cell death. Cell death was confirmed using annexin V/PI staining. For Panc 05.04, inhibition with DEAB had no effect on viability or cell death. Data represents mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined using a two-sided Student t test with P < .05 (*), P < .01 (**), P < .001 (***), and P < .0001 (****) against cells treated with gemcitabine, radiation or chemoradiation only. (E) Combined A37 and radiotherapy treatment of MiaPaCa-2 cell aggregates shows a reduction in volume of the cell aggregates at higher doses of the inhibitor. A scatter plot analysis with means ± SD (blue spots: inhibitor treatment only, red spots: A37 + radiation treatment). The bars represent mean of at least 175 replicates per condition. Statistical comparison was done between radiation treatment only vs radiation and A37 treatment using a two-sided Student t test with P < .0001 (****). A representative of each of the experimental conditions is shown in the corresponding CAMA scans.