Figure 5.
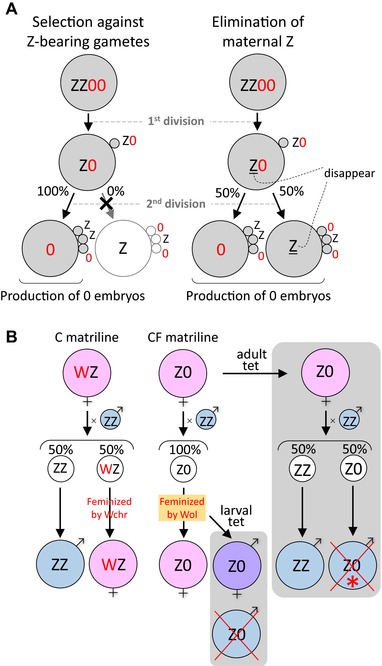
(A) Schematic illustration of two alternative mechanistic models of disruption of Z chromosome inheritance that explain the observed data. The “Selection against Z gametes” model assumes that Z‐bearing gametes are selected against during meiosis (left). The “Elimination of maternal Z” model assumes that Z chromosomes are eliminated during or after normal meiosis, while all the autosomes being intact (right). (B) All‐female production explained by Wolbachia–host interaction. Effects of wFem on the development and sex determination of E. mandarina, and outcomes of larval versus adult tet treatment are illustrated. Asterisk: The majority of Z0 males die, but a few survived.
