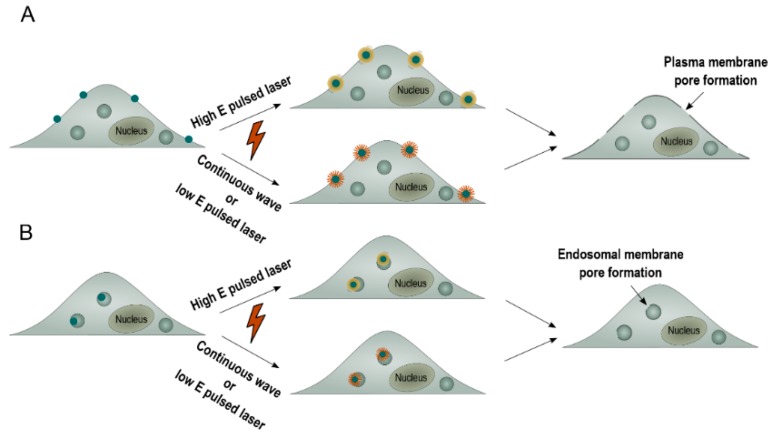
Figure 2.
The application of plasmonic NPs to overcome intracellular barriers. (A) NP-sensitized plasma membrane photoporation. Cells are incubated with plasmonic NPs to allow attachment of the NPs to the plasma membrane. Next, laser irradiation causes the formation of VNBs (high energy pulsed laser) or heating (continuous wave or low energy pulsed laser). The generation of these plasmonic effects causes the formation of a pore in the plasma membrane, which allows entry of exogeneous compounds into the cell by diffusion; (B) light-triggered endosomal escape. Plasmonic NPs are allowed to be taken up by the cell through endocytosis. Next, laser irradiation causes the formation of VNBs (high energy pulsed laser) or heating (continuous wave or low energy pulsed laser). The generation of these plasmonic effects causes the formation of a pore in the endosomal membrane, which allows release of endocytosed cargo.