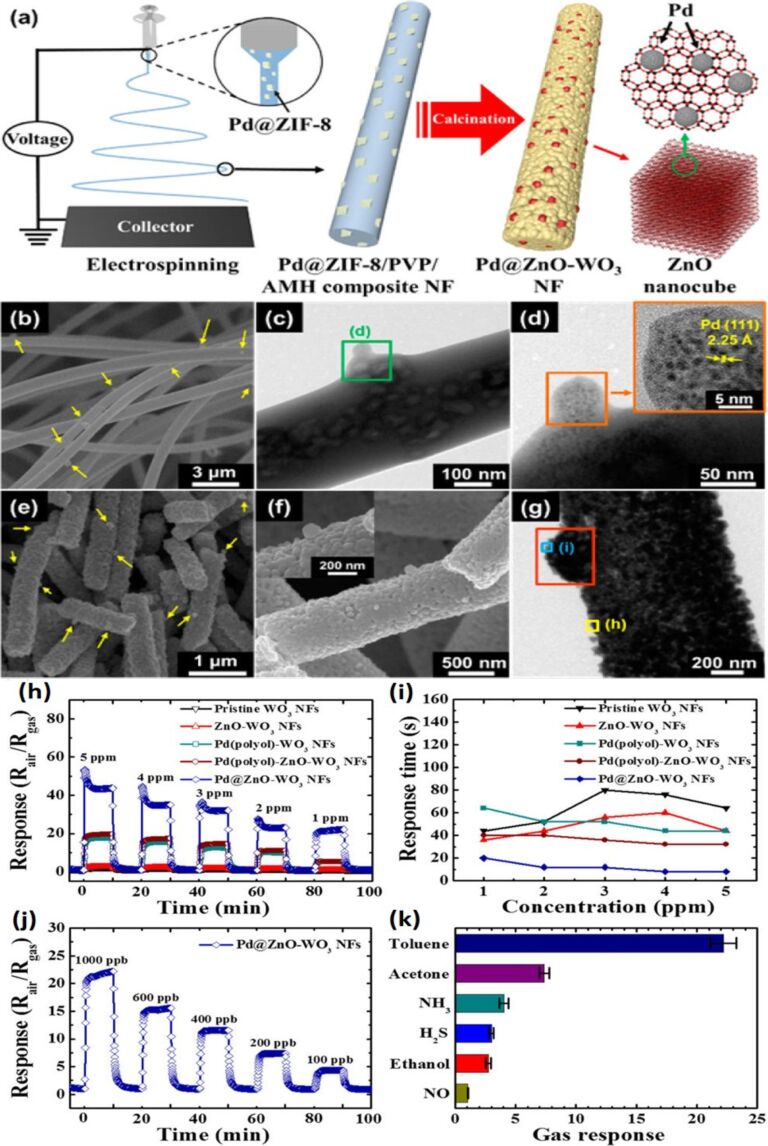
Figure 9.
(a) Schematic illustration of synthetic process for the Pd@ZnO–WO3 NFs; (b) SEM image of as-spun ammonium metatungstate hydrate (AMH)/PVP/Pd@ZIF-8 NFs; (c,d) TEM images of AMH/PVP/Pd@ZIF-8 NFs and (inset) HRTEM image; (e,f) SEM images of Pd@ZnO–WO3 NFs and (inset) magnified image of surface; (g) TEM image of Pd@ZnO–WO3 NFs, response characteristics of pristine WO3, ZnO–WO3, Pd–WO3, Pd–ZnO WO3, and Pd@ZnO–WO3 NFs toward toluene in the concentration range of 1–5 ppm at 350 °C; (h) dynamic sensing transition; (i) response time evaluation; and (j) detection limit characteristics of the Pd@ZnO–WO3 NFs toward toluene down to 100 ppb at 350 °C; (k) selective toluene detection characteristics of the Pd@ZnO–WO3 NFs with respect to the multiple interfering analytes at a concentration of 1 ppm at 350 °C. Reproduced with permission from [1], copyright 2016 ACS.