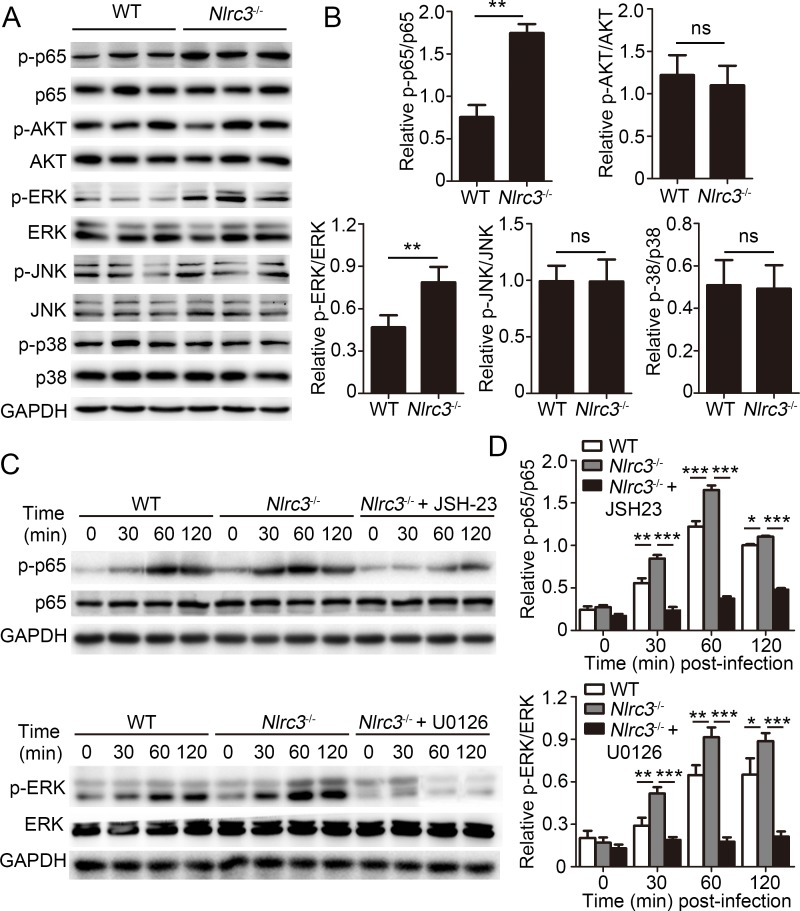
Fig 6. NLRC3 negatively regulates NF-κB and ERK Signaling in CD4+ T cells.
(A-B) Purified WT or Nlrc3-/- naïve CD4+ T cells were adoptively transferred into Rag2-/- mice. Then recipient mice were infected with M. tuberculosis and were harvested at 3w.p.i.. Lungs were collected. (A) Immunoblot analysis of lung lysates. Each lane represents an individual mouse. (B) Densitometry quantification of band intensity for A. (C-D) Purified WT and Nlrc3-/- CD4+ T cells were stimulated with anti-CD3 (1 μg/ml) plus anti-CD28 (1 μg/ml) in the presence or absence of the NF-κB inhibitor JSH-23 (20 μM) or MEK1/2-inhibitor U0126 (40 μM). (C) Lysates were probed for total and phosphorylated p65 (p-p65), p65, p-ERK, ERK and GAPDH. (D) Densitometry quantification of band intensity for C. Data shown in (B and D) are the mean ±SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001. Data are representative of three independent experiments with similar results.