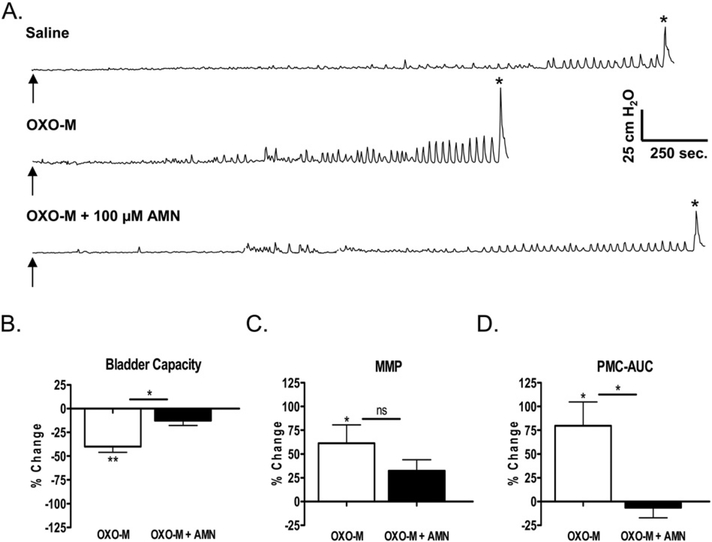
Fig. 5.
Effect of intravesical infusion of OXO-M (50 μM) and AMN on reflex bladder activity in conscious spinal cord injured cats. A. Top tracing, control saline CMG. Arrow indicates the start of infusion (2 ml/min). * indicates the first micturition contraction. Middle tracing, infusion of OXO-M reduces BC, increases MMP, and increases the amplitude of pre-micturition contractions (PMCs). Bottom tracing, infusion of AMN (100 μM) in combination with OXO-M completely blocks the effects of OXO-M. All recordings are from the same experiment. B, C, and D. Graphs summarizing the effects of AMN (50 μM or 100 μM) on the changes in CMG parameters elicited by intravesical infusion of OXO-M (50 μM). The effects of the two AMN concentrations were not significantly different; therefore, for statistical analyses, we combined the data from experiments in which either concentration of AMN was tested. Effects of OXO-M in untreated preparations (white bars) or when administered in combination with AMN (black bars) represent the percentage change from the measurements during an initial saline control CMG (n = 12 experiments in B and C, 11 experiments in D). The differences between the effects of saline and OXO-M before and after AMN were compared using repeated-measures ANOVA and Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test. Compared to saline control, OXO-M significantly decreased BC (p < 0.001) and significantly increased MMP and PMC-AUC (p < 0.05). AMN treatment significantly (p < 0.05) reduced the effects of OXO-M on BC and PMC-AUC but did not significantly suppress the effect on MMP.