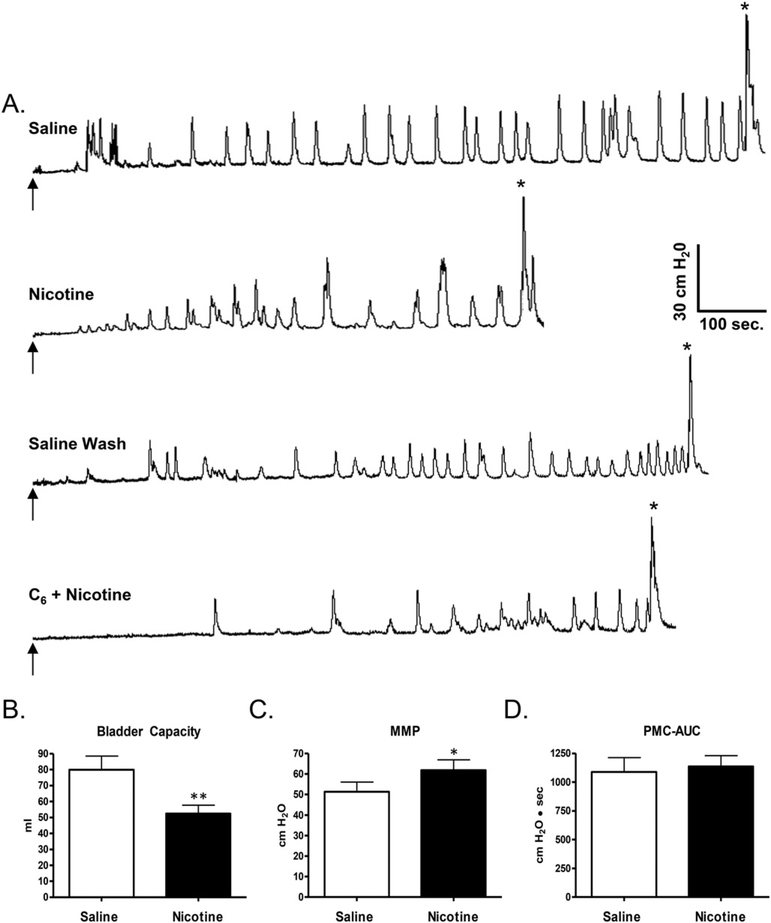
Fig. 8.
A. Effect of intravesical infusion of nicotine (250 μM) on reflex bladder activity in a conscious spinal cord injured cat. Top tracing, control saline CMG. Arrow indicates the start of infusion (2 ml/min).* indicates the first micturition contraction. Second tracing, infusion of nicotine reduces BC but does not influence the frequency or amplitude of pre-micturition contractions. Third tracing, intravesical infusion of saline reverses the effect of nicotine. Bottom tracing, intravesical infusion of hexamethonium (C6, 1 mM) in combination with nicotine suppresses the nicotine-induced reduction in BC. All recordings are from the same experiment. B, C, and D. Graphs summarizing the effects of nicotine (250 μM) on the CMG parameters (n = 16). Intravesical infusion of nicotine significantly reduced bladder capacity (B, p < 0.001, paired t-test), significantly increased MMP (C, p < 0.05, paired t-test) but did not significantly change PMC-AUC (D, p > 0.05, paired t-test).