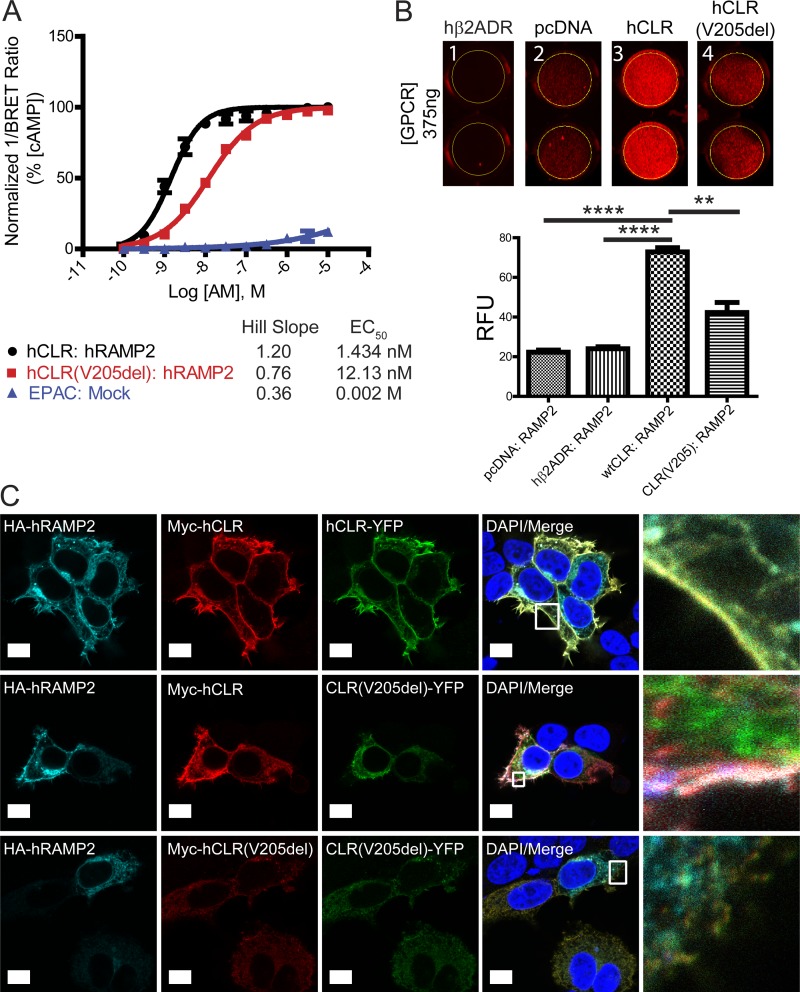
Figure 3.
hCLR (V205del) exhibits impaired signaling and plasma membrane localization. (A) Detection of cAMP production with the EPAC biosensor after 45 min of AM stimulation of hCLR:hRAMP2 or hCLR(V205del):hRAMP2. n = 5 independent experiments, in duplicate. (B) Infrared 24-well plate imaging of transiently transfected HEK293T cells with MarsCy1(FAP)-tagged hRAMP2. Cells transfected with 375 ng of pcDNA3.1, hβ2ADR, hCLR, and hCLR (V205del) were cotransfected with FAP-tagged RAMP2 and cells were stained with the MarsCy1 and membrane impermeant fluorogen SCi1. Compare cell surface expression to the pcDNA negative control. SCi1 stained cells were scanned at 700 nm (red, SCi1). n = 5 independent experiments, in duplicate. (C) Confocal microscopy of HEK293T cells expressing HA-hRAMP2 (cyan), Myc-hCLR (red), and hCLR-YFP (green). The top row shows the colocalization of all three wild-type proteins at the plasma membrane resulting in yellow-cyan color. The middle row shows the changes in protein distribution with coexpression of hCLR (V205)-YFP protein: wild-type HA-RAMP2 and Myc-hCLR colocalize to the plasma membrane (white merge), while the distribution of the hCLR (V205)-YFP protein (green) remains largely intracellular. The bottom row shows complete absence of all three proteins at the plasma membrane when both mutant forms of the hCLR(V205) receptor are expressed. Far right column shows the boxed regions at higher magnification. n = 2 independent experiments, with analysis of >50 cells per condition. Bar, 10 µm. **, P < 0.01; ****, P < 0.0001.