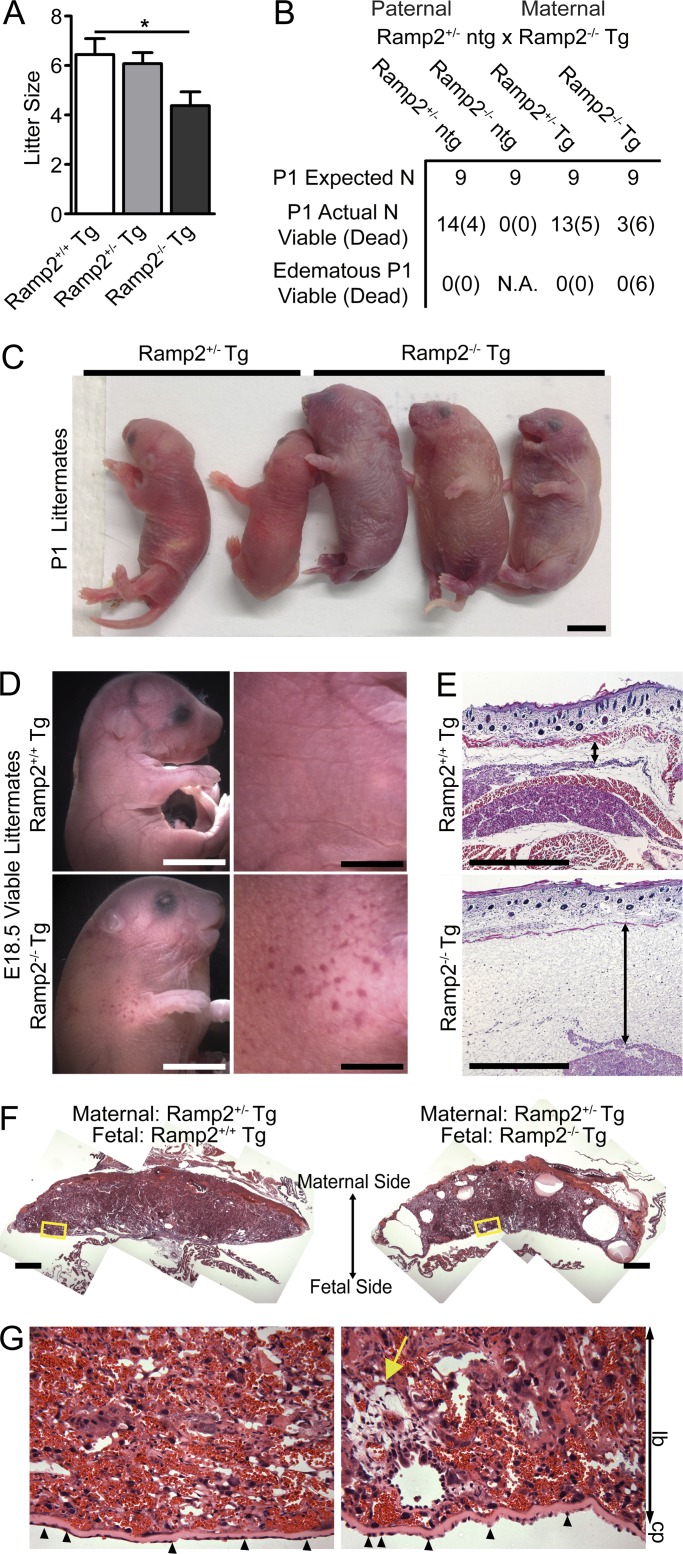
Figure 7.
Genetic loss of Ramp2 leads to subfertility, perinatal HF, and lethality. (A) Litter sizes from Ramp2+/− ntg males crossed with Ramp2+/+Tg, Ramp2+/−Tg, and Ramp2−/−Tg females. n = 8–12 litters per genotype. Significance was determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s Multiple Comparison test. (B) Breeding results, both expected and observed Mendelian ratios from Ramp2+/− ntg male crossed to Ramp2−/−Tg female. n = 45 from 8 litters. (C and D) Representative images of P1 (C) and E18.5 Ramp2−/−Tg (D) mice compared with littermate controls. Bars, 5 mm. (E and F) Representative histological images of skin (E) and placenta (F) from E18.5 Ramp2+/+Tg and edematous Ramp2−/−Tg littermates. Double-sided arrow indicates subcutaneous edema. Bars, 500 µm. (G) Higher magnification of boxed regions from panel F. Yellow arrow points to fluid filled edematous regions. Small arrowheads indicate abnormally shaped trophoblast cells lining the chorionic plate. lb, labyrinth; cp, chorionic plate. Bars, 100 µm.