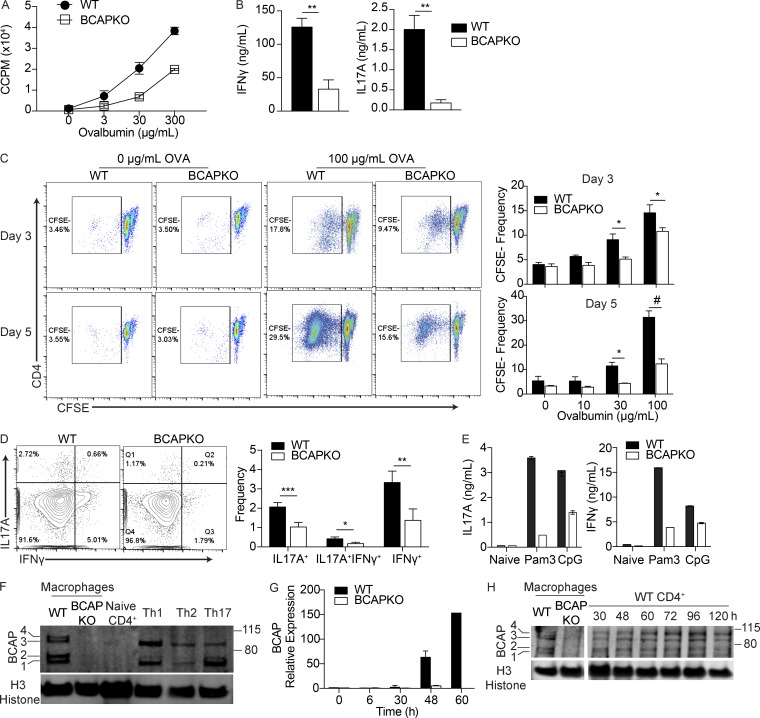
Figure 1.
BCAP is required for efficient T cell priming and effector function. (A) CD4+ T cells were isolated from popliteal and inguinal lymph nodes of OVA-immunized WT and BCAPKO mice. Purified T cells pooled from three mice were incubated with WT DCs (5:1) and indicated concentrations of OVA. Proliferation was measured by 3H incorporation in the last 16 h of culture. CCPM, cell counts per minute. Shown is the mean ± SD of three technical replicate cultures. Data are representative of three independent experiments. (B) Analysis of IFN-γ and IL-17A in the supernatant of DC–T cell cocultures as in A with 100 µg/ml OVA. Shown is the mean ± SEM; n = 4 mice per group. **, P < 0.01. Statistical analysis was performed with the two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test. (C) Representative flow plots (left) and quantification (right) of CD4+ T cell CFSE dilution after 3 d or 5 d of in vitro restimulation with WT DCs and indicated concentrations of OVA. Shown is the mean ± SEM; n = 4. Statistical analysis was performed with two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test. *, P < 0.05; #, P < 0.0001. (D) Representative flow cytometry (left) and quantification of intracellular cytokine staining (right) of CFSEnegCD4+ T cells after 5 d of DC–T cell coculture with 100 µg/ml OVA. Shown is the mean ± SEM; n = 4 mice per group. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. Statistical analysis was performed with the two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test. (E) WT and BCAPKO naive CD4+ T cells pooled from three mice were incubated with WT DCs (5:1) and stimulated with the TLR ligands Pam3CSK4 (100 ng/ml) or CpG (1 µM). After 5 d, supernatant IL-17A and IFN-γ levels were measured by ELISA. Shown is the mean ± SD. Data are representative of three independent experiments. (F) Lysates from WT and BCAPKO bone marrow–derived macrophages and WT CD4+ T cells polarized to Th1, Th2, or Th17 cells were analyzed for BCAP expression by Western blotting. Data are representative of four independent experiments. (G) WT and BCAPKO naive T cells were polarized to Th17 for the indicated time and analyzed for BCAP expression using qPCR. Expression is relative to WT 0 h. Data are representative of three independent experiments. (H) Lysates from WT and BCAPKO bone marrow–derived macrophages and WT CD4+ T cells polarized to Th17 cells for the indicated time points were probed for BCAP expression by Western blotting. Data are representative of three independent experiments.