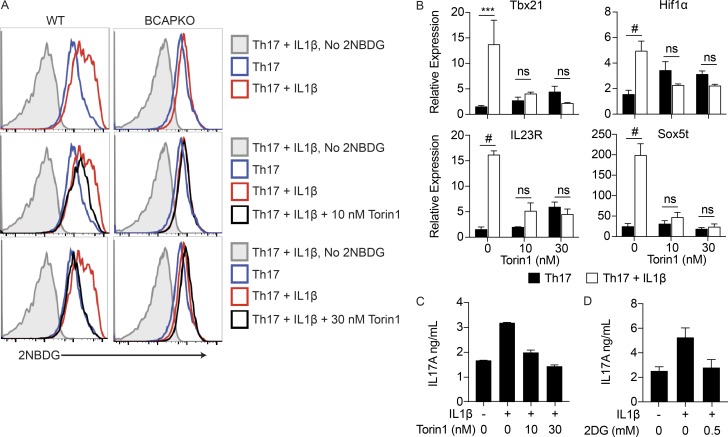
Figure 7.
IL-1β mediated increases in glycolysis, and the generation of pathogenic Th17 cells is completely abrogated by low levels of mTOR and glycolysis inhibition. (A) Naive WT and BCAPKO CD4+ T cells were polarized to Th17 cells for 48 h, and then pretreated with 10 or 30 nM Torin1 for 1 h. After pretreatment, the indicated cells were stimulated with 10 ng/ml IL-1β and assayed with 2NBDG 24 h later to quantify glucose uptake via flow cytometry. Data are representative of three independent experiments. (B) Naive WT CD4+ T cells were polarized to Th17 cells for 48 h, and then pretreated with 10 nM or 30 nM Torin1 for 1 h. After pretreatment, the indicated cells were stimulated with 10 ng/ml IL-1β for 6 h and analyzed for pathogenic Th17 transcripts using qPCR. Shown is the mean ± SEM; n = 2. ***, P < 0.001; #, P < 0.0001. Statistical analysis was performed with the two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test. (C and D) Naive WT CD4+ T cells were polarized as in B, and then pretreated with Torin1 or 2DG for 1 h, and stimulated with 10 ng/ml IL-1β for 6 h. Supernatants were collected to determine levels of IL-17A secretion by ELISA. Shown is the mean ± SD of technical replicates. Data are representative of three independent experiments.