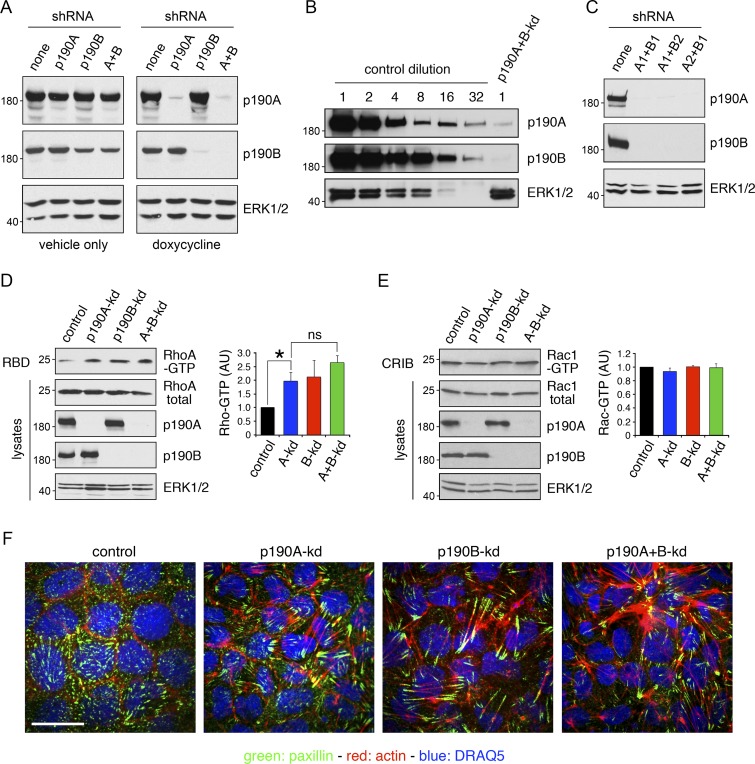
Figure 2.
p190A and/or p190B repress Rho signaling in epithelial cells. (A) MDCK TR-T10 cells expressing inducible shRNAs targeting p190A and/or p190B. Cells were incubated with either vehicle or doxycycline (dox) to induce knockdown of gene expression. Cells were cultured for 3 d at sparse density to achieve optimal knockdown followed by 5 d at high density. Whole-cell lysates were then subjected to Western blotting to detect p190A, p190B, or ERK1/2. All other figures show data from doxycycline-treated cells only. (B) Whole-cell lysates from control cells were subjected to serial twofold dilution. These samples, along with undiluted lysates from p190A+B-kd cells, were processed for Western blotting to detect p190A, p190B, and ERK1/2. (C) Knockdown of gene expression using different combinations of shRNAs targeting p190A or p190B. (D) Effects of p190A and/or p190B depletion on cellular RhoA-GTP levels were measured by a Rhotekin–RBD pulldown assay. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3); *, P < 0.05 (n = 3). (E) Rac1-GTP levels in cells with p190A-kd and/or p190B-kd were determined by a PAK3-CRIB pulldown assay. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3); *, P < 0.05 (n = 3). Molecular masses are given as kilodaltons. (F) Control, p190A-kd, p190B-kd, or p190A+B-kd cells were processed to localize the focal adhesion constituent paxillin (green), incubated with Alexa Fluor 594–phalloidin to detect polymerized actin (red), and stained with the DNA-intercalating dye DRAQ5 to show nuclei (blue). Bar, 10 µm.