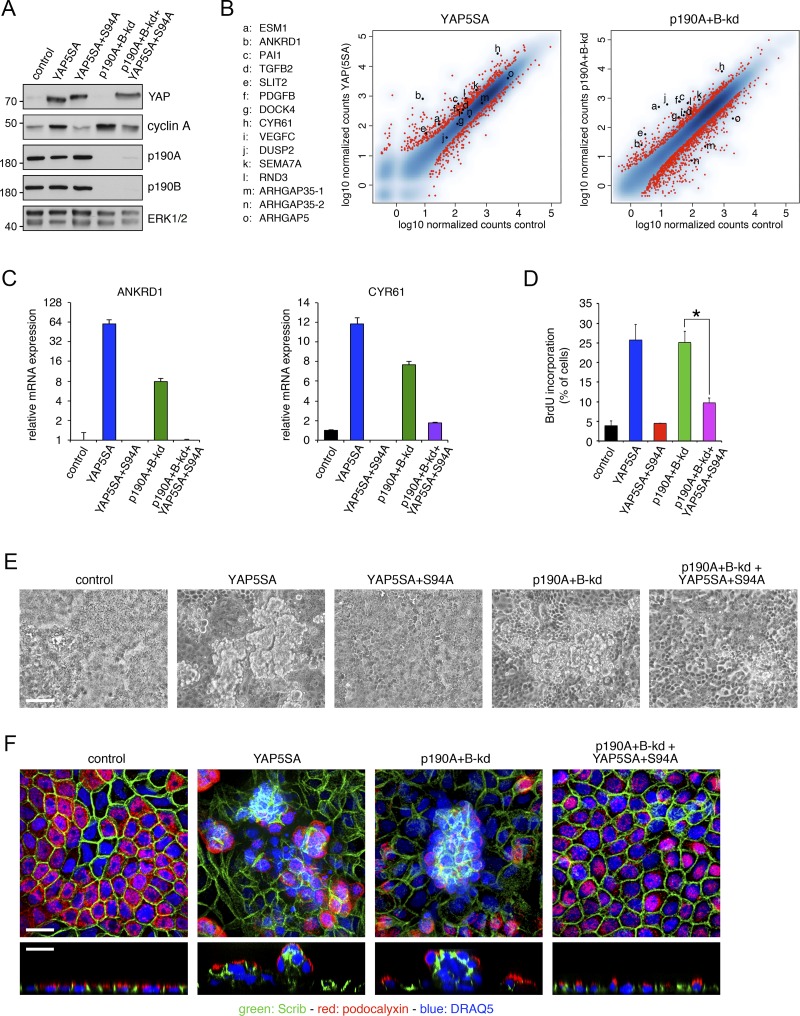
Figure 5.
p190A and p190B promote CIP by repressing YAP-mediated gene transcription. (A) Expression of constitutively active YAP5SA or dominant-negative YAP5SA+S94A in control and p190A+B-kd MDCK cells. Western blotting of whole-cell lysates was performed to detect YAP1, cyclin A, p190A, p190B, and ERK. Molecular masses are given as kilodaltons. (B) mRNA-seq transcriptomes from dense cultures of MDCK cells expressing constitutively active YAP5SA and from p190A+B-kd cells were derived from samples processed concomitantly to permit direct comparison. The data are represented as described in the legend to Fig. 5 A. (C) qPCR analysis of ANKRD1 and CYR61 expression in control and p190A+B-kd cells with or without expression of YAP5SA or YAP5SA+S94A. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). (D) BrdU incorporation in dense cultures of control and p190A+B-kd cells with or without expression of YAP5SA or YAP5SA+S94A. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 4); *, P < 0.01. (E) Phase-contrast imaging of control, YAP5SA, YAP5SA+S94A, and p190A+B-kd cells as well as p190A+B-kd cells expressing YAP5SA+S94A. Bar, 50 µm. (F) Confocal microscopy of control, YAP5SA, and p190A+B-kd cells as well as p190A+B-kd cells expressing YAP5SA+S94A. Cells were labeled to detect Scrib (green) and podocalyxin (red), and nuclei were stained with DRAQ5 (blue). Bars, 10 µm.