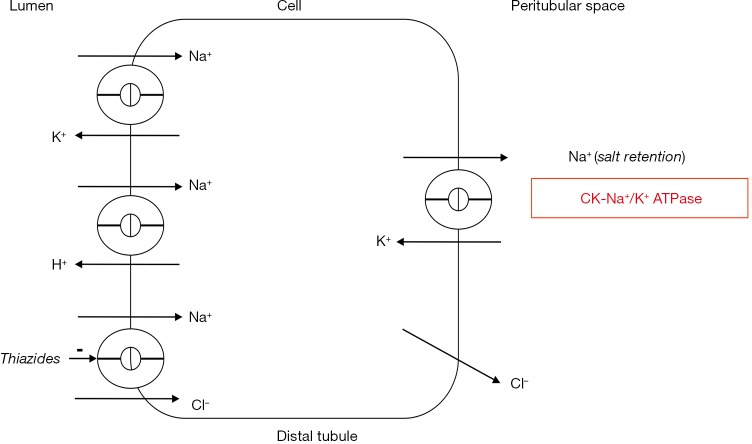
Figure 5.
Creatine kinase and sodium retention. Renal sodium retention is driven by basolateral Na+/K+ ATPase (15). Depicted is the kidney distal convoluted tubule. Creatine kinase (CK) is tightly bound near basolateral Na+/K+ ATPase to regenerate ATP for sodium retention (17,53). Thiazide diuretics may antagonize this effect indirectly as these drugs inhibit luminal Na+/Cl−-cotransport (53,57).