Fig. 6. CRSBP-1 ligands stimulate contraction of the CRSBP-1-associated ER network in SVEC4–10 cells in a CRSBP-1-dependent manner.
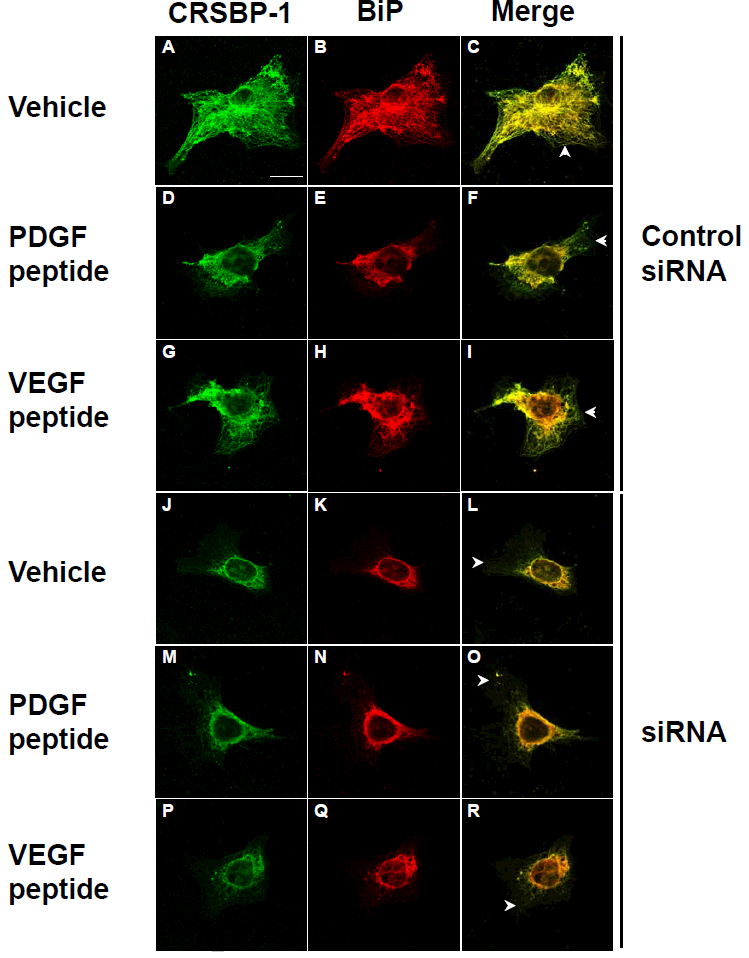
Cells transfected with control siRNA (panels A to I) and CRSBP-1 siRNA (panels J to R) were stimulated with vehicle only (panels A, B, C and panels J, K, L), 10 μM PDGF peptide (panels D, E, F and panels M, N, O) and 10 μM VEGF A peptide (panels G, H, I and panels P, Q, R) for 1 h. After stimulation, cells were fixed with methanol at −20°C for 10 min and stained with anti-CRSBP-1 serum (panels A, D, G, J, M and P) and anti-BiP (the ER marker) antibody (panels B, E, H, K, N and Q), then visualized with a confocal microscope. Cells treated with vehicle only and CRSBP-1 ligands showed intracellular co-localization of CRSBP-1 and BiP (panels C, F, I, L, O and R). As described previously (12), about 80% of CRSBP-1 protein was down-regulated by transfection of SVEC4–10 cells with CRSBP-1 siRNA compared with those of cells transfected with control siRNA. CRSBP-1 ligands stimulated contraction of the ER network in cells transfected with control siRNA (panels D to I vs panels A, B and C). Down regulation of CRSBP-1 protein by CRSBP-1 siRNA transfection abolished CRSBP-1 ligand-stimulated contraction of the ER network in these cells (panels M to R vs. panels J, K and L). Cells transfected with CRSBP-1 siRNA exhibited constitutive contraction of the ER network (panels J to R vs. panels A, B and C). Arrowheads indicate the plasma membrane localization of CRSBP-1.
