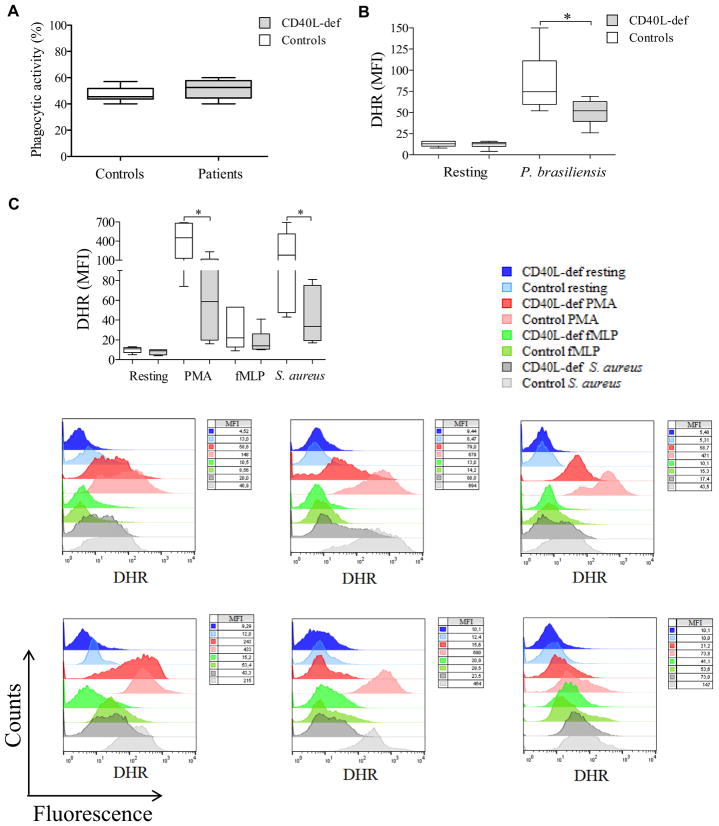
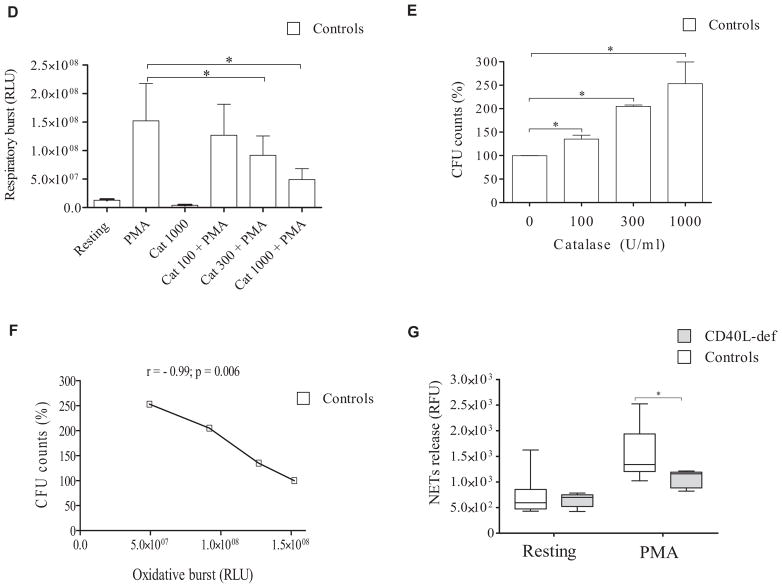
FIG 1.
Defective respiratory burst in the seting of CD40L deficiency and its relation to neutrophil microbicidal activity. A, Neutrophils from CD40L-deficient patients (n = 6) exhibit normal phagocytic capacity compared with those from healthy control subjects. B and C, The neutrophil respiratory burst from CD40L-deficient patients was assessed by using dihydrorhodamine (DHR) analysis in response to P brasiliensis (Fig 1, B), as well as PMA, fMLP, or S aureus (Fig 1, C), from 6 independent experiments comparing each CD40L-deficient patient with different healthy control subjects. Results were expressed as MFI (n = 6; *P ≤ .05, Mann-Whitney test). D, Respiratory bursts from neutrophils from healthy control subjects treated with various concentrations of catalase were analyzed by using luminol-enhanced chemiluminescence; values were expressed as relative light units (RLU). E, After challenging neutrophils with P brasiliensis (ratio of 2 neutrophils/1 fungus), microbicidal activity was assessed based on CFU values from recovering internalized fungi. CFU values (percentage of controls) were determined in relation to CFU numbers of untreated neutrophils from healthy control subjects. Both the respiratory burst and microbicidal activity of neutrophils from healthy control subjects were assessed in the presence of different doses of catalase (100, 300, and 1000 U/mL). F, Correlation between respiratory burst (data set from Fig 1, D) and microbicidal activity (data set from Fig 1, E) reduction was assessed by using Pearson correlation analysis (n = 3). G, Quantification of NETs release by isolated neutrophils from CD40L-deficient patients in comparison with healthy control subjects. After incubation for 4 hours in the presence of PMA, NET release (n = 5) was analyzed by using Sytox Orange, and results were expressed in relative fluorescence units (RFU), as previously described.62 Patient 4 died before NET analysis was available. Significant differences are denoted by asterisks at a P value of .05 or less (Mann-Whitney test).