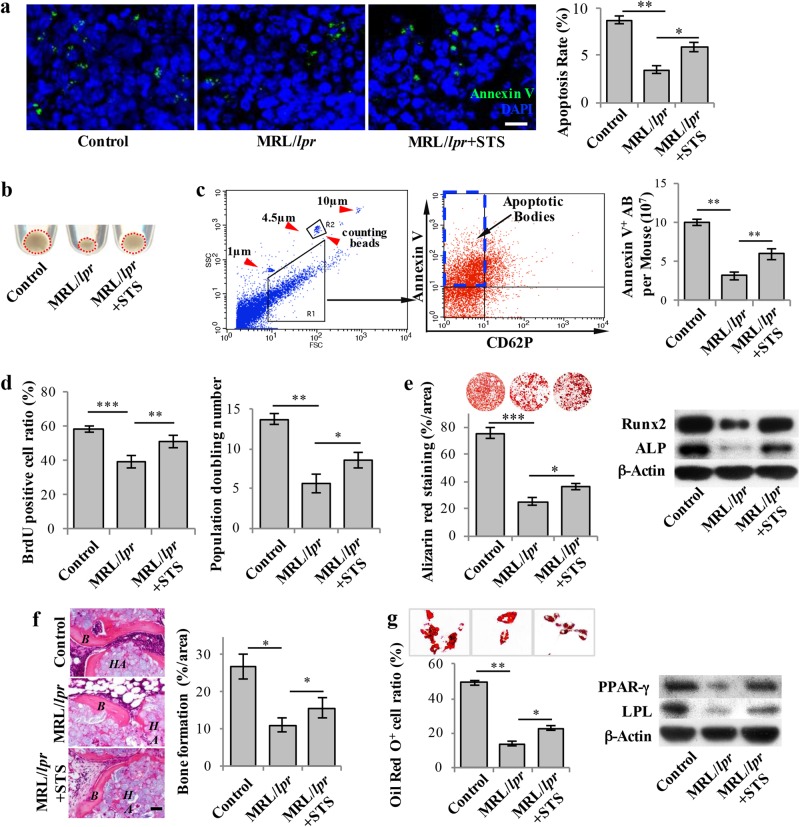
Fig. 1.
Staurosporine-induced elevated levels of apoptotic bodies rescued impaired MSCs in MRL/lpr Mice. a 3 ng of Staurosporine (STS) was intraperitoneally administered to MRL/lpr mice twice a week for 4 weeks (total of 8 injections). Annexin V was injected via the tail vein 2 h prior to sample collection to assess the apoptosis rate in the bone marrow. Immunostaining showed that STS injection rescued the reduced number of apoptotic cells in the bone marrow of MRL/lpr mice (n = 5). b Fewer apoptotic body-sized extracellular vesicles were observed in pellets derived from MRL/lpr mice (n = 5) than in those collected from the control mice. After 4 weeks of STS treatment, the amount of apoptotic body-sized extracellular vesicles was increased in MRL/lpr mice. c The number of apoptotic bodies was counted by flow cytometry. 1 and 10 μm diameter beads and 4.5 μm counting beads were used to gate 1–5 μm-sized microvesicles. Annexin V+ and CD62P− events were counted as apoptotic bodies. The flow cytometric calculation showed that the number of apoptotic bodies from the bone marrow of MRL/lpr mice (n = 5) was reduced compared to the wild-type control group. After 4 weeks of STS treatment, the number of apoptotic bodies from the bone marrow of MRL/lpr mice (n = 5) was increased. d BrdU labeling and continuous passage assay showed that MRL/lpr MSCs (n = 5) had reduced proliferation and population doubling rates when compared to the wild-type control group. After 4 weeks of STS treatment, proliferation and population doubling rates were increased in MRL/lpr MSCs (n = 5). e Compared to wild-type MSCs, MRL/lpr MSCs showed reduced capacities to form mineralized nodules when cultured under the osteogenic inductive conditions, assessed by alizarin red staining (n = 5), and reduced expression of osteogenic markers Runx2 and ALP, assessed by Western blot. After 4 weeks of STS treatment, reduced mineralized nodule formation and expression of Runx2 and ALP were rescued in MRL/lpr MSCs (n = 5). f MRL/lpr MSCs showed reduced capacities to form new bone when implanted into immunocompromised mice subcutaneously using HA/TCP as a carrier. After 4 weeks of STS administration, reduced bone formation capacity was rescued in MRL/lpr MSCs (n = 5). H&E staining showed new bone (B) and HA/TCP (HA) carrier. g Compared to wild-type MSCs, MRL/lpr MSCs showed a reduced capacity to differentiate into adipocytes when cultured under the adipogenic inductive conditions, as assessed by Oil red O staining (n = 5), along with reduced expression of adipogenic markers PPARγ and LPL, as assessed by Western blot. After 4 weeks of STS administration, reduced adipocyte formation and expression of PPARγ and LPL were rescued in MRL/lpr MSCs (n = 5). All results are representative of data generated in three independent experiments. Error bars represent the S.D. from the mean values. ***P < 0.001; **P < 0.01; *P < 0.05. Scale bar, 5 μm (a), 50 μm (f)