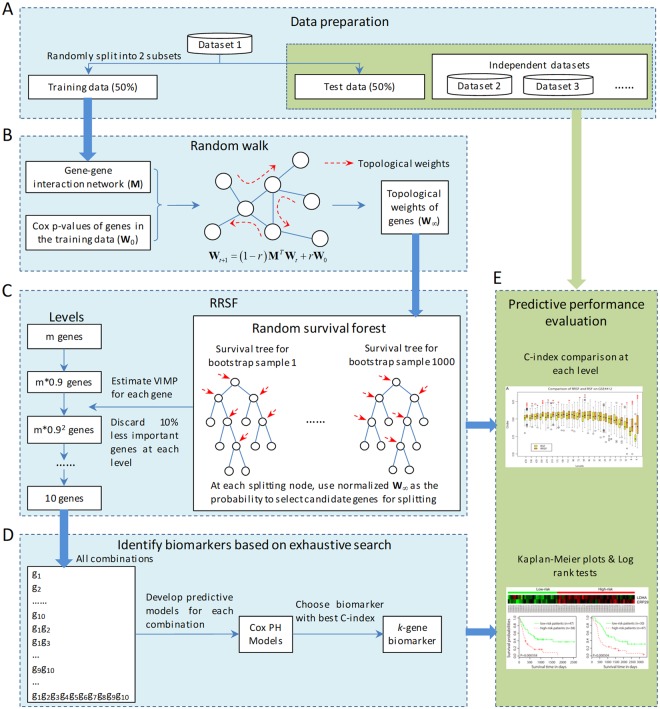
Figure 1.
The pipeline to evaluate the predictive performance of RRSF. (A) Data preparation. Dataset 1 was randomly split into a training set (50%) and a test set (50%). The training set was used to train the RRSF model, while the test set and independent datasets were used to evaluate its predictive performance. (B) Topological weights of genes were inferred using DRW. (C) Selection process for genes with best predictive performance. The number of genes were narrowed down by several iterative steps, in which, according to their VIMPs, genes ranking in the lowest 10% in terms of importance were discarded at each step. (D) Development of predictive models for all combinations of the 10 genes. Biomarkers with the highest C-index were identified. (E) Evaluation of predictive performance by C-index, Kaplan–Meier curves, and log-rank tests.