Fig. 1.
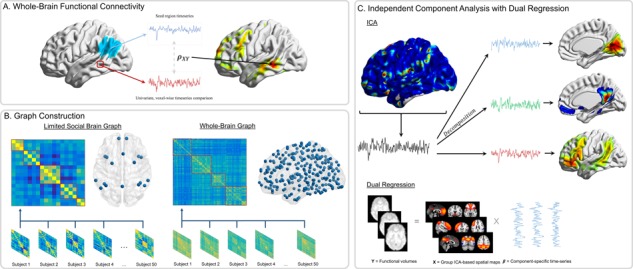
Functional connectivity approaches. (A) Whole-brain functional connectivity utilizing PPI is a voxel-wise method. The average time-series is extracted from the seed region (blue), and then time-series from each voxel (e.g. red) are compared using time-series correlations (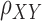 ). These correlation values are mapped onto the whole-brain statistic map. (B) Graph construction involves calculating time-series correlations between each pair of nodes (either 18 or 282) to construct individual subject correlation matrices. Individual matrices are then averaged together and community detection algorithms are applied to the group-level matrices to group nodes into functional networks (indicated by red boxes). (C) ICA utilizes multivariate mixture modeling in order to group voxel time-series into functional units. Time-series from all voxels in the brain are added to the mixture model and then decomposed into spatial maps of voxels which have similar time-series features. These group-level maps (X) are then used in the Dual Regression analyses to extract component-specific time-series (
). These correlation values are mapped onto the whole-brain statistic map. (B) Graph construction involves calculating time-series correlations between each pair of nodes (either 18 or 282) to construct individual subject correlation matrices. Individual matrices are then averaged together and community detection algorithms are applied to the group-level matrices to group nodes into functional networks (indicated by red boxes). (C) ICA utilizes multivariate mixture modeling in order to group voxel time-series into functional units. Time-series from all voxels in the brain are added to the mixture model and then decomposed into spatial maps of voxels which have similar time-series features. These group-level maps (X) are then used in the Dual Regression analyses to extract component-specific time-series (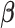 ) from each individual’s functional volumes (Y).
) from each individual’s functional volumes (Y).
