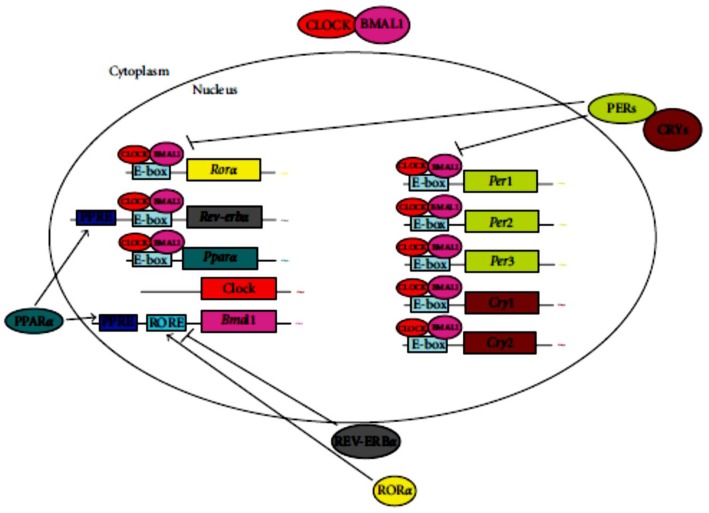
Fig. 2:
The core mechanism of the mammalian circadian clock and its link to energy metabolism. The cellular oscillator is composed of a positive limb (CLOCK and BMAL1) and a negative limb (CRYs and PERs). CLOCK and BMAL1 dimerize in the cytoplasm and translocate to the nucleus (5)