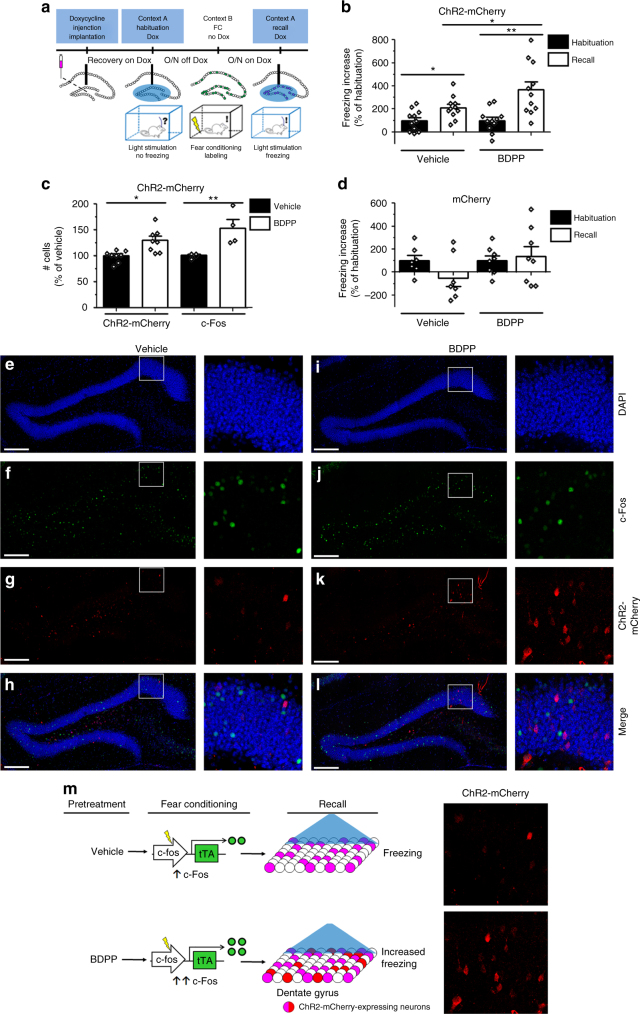
Fig. 4.
Treatment with BDPP promotes fear memory recall through upregulation of c-Fos. a Training scheme. After recovery from surgery, mice are treated with BDPP or vehicle for 2 w prior to training in CFC. b Increase in freezing upon light stimulation in Habituation and Recall sessions for mice injected with AAV9-TRE-ChR2-mCherry. Untreated and BDPP-treated mice both show an increase in freezing behavior in the Recall session, but the increase is greater in mice treated with BDPP. Recapitulation of freezing is normalized to the increase in freezing in the light-on period of the Habituation session (100%; one-way ANOVA, n = 11 per group). c Number of neurons in the DG of hippocampal sections from untreated and BDPP-treated mice expressing c-Fos and ChR2-mCherry (one-way ANOVA, n = 4,8 per group). d Increase in freezing upon light stimulation in Habituation and Recall sessions for mice injected with AAV9-TRE-mCherry. Mice do not show an increase in freezing behavior upon light stimulation in the Habituation or Recall session, regardless of treatment. Recapitulation of freezing is normalized to the increase in freezing in the light-on period of the Habituation session (100%; one-way ANOVA, n = 7–8 per group). e–l Representative images of the DG of hippocampal sections from vehicle-treated (e–h) and BDPP-treated (i–l) mice. The rectangular area in e–l is magnified to demonstrate localization of ChR2-mCherry and c-Fos in representative neurons. Scale bar: 200 µm. m Mechanism through which dietary polyphenols promote recruitment to a ChR2-mCherry-labeled memory engram. Treatment with dietary polyphenols stimulates c-fos promoter activity in the DG, resulting in expression of ChR2-mCherry upon withdrawal of Dox and training through CFC. Upon light stimulation in the Recall session, more neurons are labeled with ChR2-mCherry, resulting in increased freezing during the light-on period