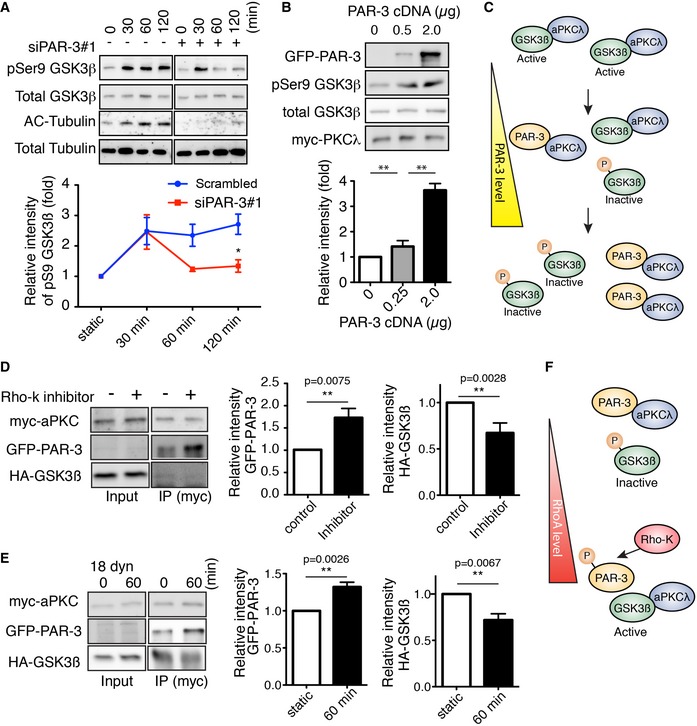
Western blotting of ECs transfected with control scrambled siRNA (indicated as “‐” in the figure) or siPAR‐3#1 and exposed to 18 dyn/cm2 laminar flow.
HEK293 cells were transfected with different amounts of GFP‐PAR‐3 cDNA with HA‐GSK3β and myc‐aPKCλ and were analyzed by Western blotting.
Model for PAR‐3‐mediated GSK3β inactivation. The balance between PAR‐3/aPKCλ complex versus the aPKCλ/GSK3β complex controls GSK3β activity.
HUVECs were transfected with indicated cDNAs and were treated with or without Rho‐kinase inhibitor (Y‐27632, 20 μM). After immunoprecipitation with indicated antibodies, samples were analyzed by Western blotting.
HUVECs were transfected with indicated cDNAs, seeded in the flow chamber, and exposed to 18 dyn/cm2 laminar flow for 60 min. After immunoprecipitation with anti‐myc antibody, samples were analyzed with indicated antibodies by Western blotting. Relative intensity of each signal was statistically analyzed.
RhoA/Rho‐kinase pathway controls GSK3β activity by modulating balance between the PAR‐3/aPKCλ complex versus the aPKCλ/GSK3β complex.
Data information: In (A, B, D, and E), data are presented as mean ± SEM (A and B,
n = 3; D and E,
n = 5). ns: not significant;
P ≥ 0.05; differences *
P < 0.05, **
P < 0.01, analyzed with two‐way ANOVA with Bonferroni multiple comparison
post hoc analysis (A), one‐way ANOVA followed with Tukey's multiple comparison
post hoc analysis (B), or Mann–Whitney U test (D, E).