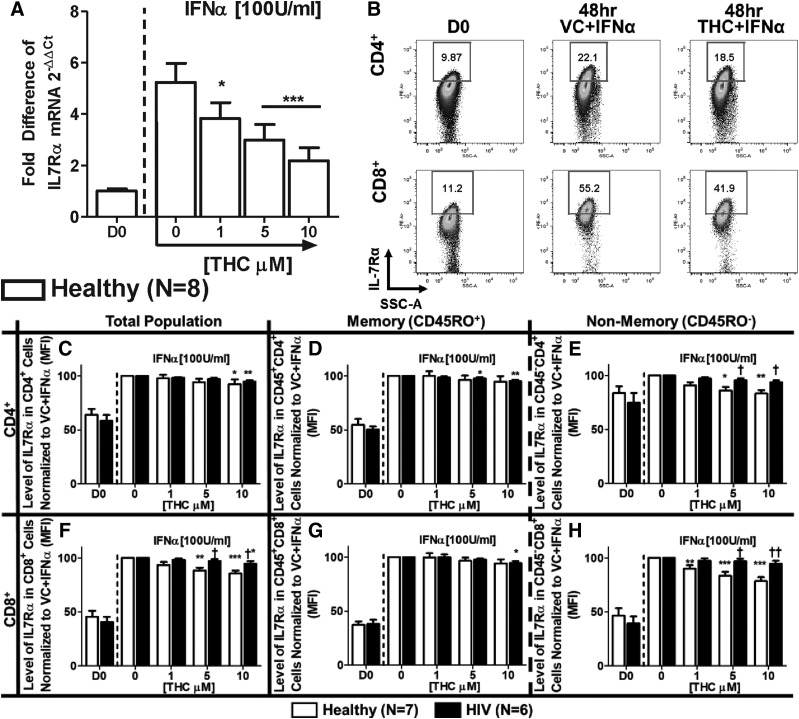
Fig. 3.
THC suppresses IFNα-induced expression of IL-7Rα mRNA in T cells from healthy donors but differentially affects IFNα-induced surface expression of IL-7Rα in T cells from healthy vs. HIV+ T donors. (A) To determine the effects of IFNα and THC on IL-7Rα mRNA expression, T cells were purified from healthy donors, and treated with either vehicle (0.03% EtOH) or various concentrations of THC (1, 5, or 10 µM) for 30 minutes. After treatment, cells were stimulated with IFNα (100 U/ml), incubated for 48 hours, and harvested for quantification of IL-7Rα mRNA levels by real-time quantitative PCR. For the determination of IL-7Rα surface expression, PBMCs from healthy and HIV+ donors were isolated through Ficoll Paque density gradient centrifugation and either immediately stained for CD3, CD4, CD8, CD45RO, and IL-7Rα (D0) or treated with THC and IFNα, as described above, and measured for IL-7Rα expression after 48 hours. (B) Example of IFNα-mediated IL-7Rα expression and THC (10 µM)-mediated suppression in a healthy donor. The effects of THC on the expression level [mean fluorescence intensity (MFI)] of IL-7Rα in T cells from healthy and HIV+ donors in total (C), memory (D), and nonmemory (E) CD4+ cells; and total (F), memory (G), and nonmemory (H) CD8+ cells. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences of the treatment with the HIV status–matched VC (0 THC) (*P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001). Daggers indicate statistically significant differences of treatment-matched groups between Healthy and HIV+ T cells (†P ≤ 0.05; ††P ≤ 0.01) (two-way analysis of variance with Bonferroni multiple-comparisons post-test). D0, day 0; SSC-A, side scatter area.