Fig. 6.
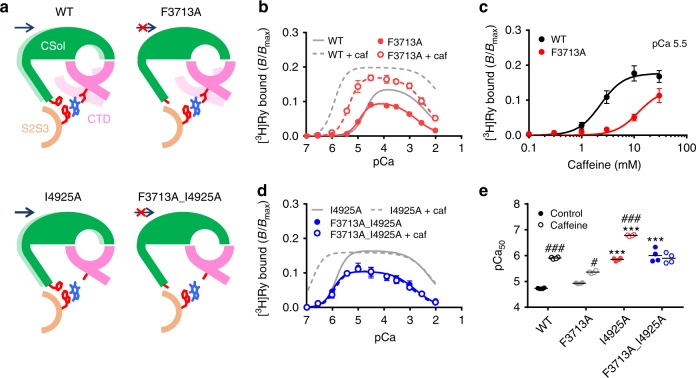
Verification of interaction between tryptophan and phenylalanine in the putative caffeine-binding site. a Schematic diagrams of conformation of Ca2+-binding and caffeine-binding sites for WT, F3713A, I4925A and F3713A_I4925A in the presence of caffeine with expected interactions and movement of the CSol and CTD. Light colors indicate locations of the CSol and CTD in the absence of caffeine. Caffeine shifts the CSol rightward in WT and I4925A via the interaction between tryptophan and phenylalanine, but not in F3713A or F3713A_I4925A because of loss of the phenylalanine residue. b Ca2+-dependent [3H]ryanodine binding to F3713A with (open circles) or without (closed circles) 10 mM caffeine. The Ca2+ sensitization of F3713A by caffeine was about half that of WT. Data are given as mean ± SEM (n = 4). c Caffeine-dependent activation of [3H]ryanodine binding to WT and F3713A at pCa 5.5. F3713A showed lower sensitivity to caffeine than WT. Data are given as mean ± SEM (n = 4). d Ca2+-dependent [3H]ryanodine binding to F3713A_I4925A with (open circles) or without (closed circles) 10 mM caffeine. Data are given as mean ± SEM (n = 4). e Summary of pCa50 values of WT and the mutants with (hatched columns) or without (open columns) 10 mM caffeine. Data are given as mean (horizontal bar) and individual values (circles). * and *** indicate statistical significance with p < 0.004 and p < 0.0001, respectively, vs WT using one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s post hoc test. ###p < 0.0001 vs control using unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test