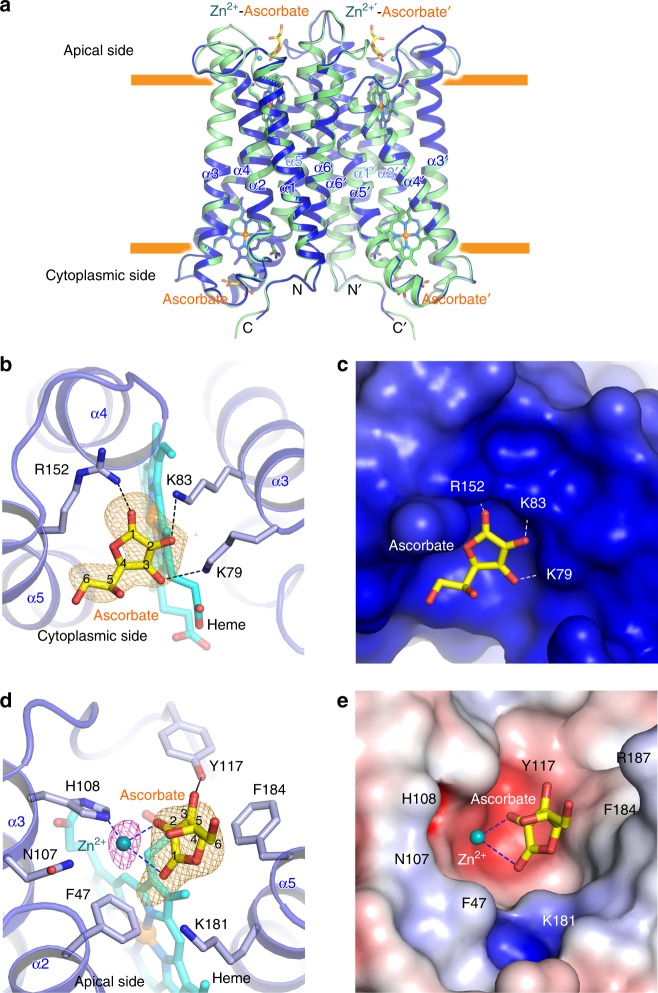
Fig. 2.
Substrate-bound structure of Dcytb. a The six α-helices of the substrate-free (green) were superimposed on those of the substrate-bound structure (blue) with an r.m.s.d. of 0.4 Å for all Cα atoms. b Ascorbate is bound on the cytoplasmic surface of Dcytb by interacting with three positively charged residues. The omit map for ascorbate is contoured at 2.5σ (orange mesh). c The negatively charged cavity for ascorbate-binding on the cytoplasmic surface is shown. d The Zn2+ binding to H108 and two hydroxyl groups of ascorbate on the apical surface of Dcytb is shown. The anomalous difference Fourier map (magenta mesh) calculated from X-ray data collected at 1.0 Å is contoured at 3.5σ. The omit map for ascorbate (orange mesh) bound to the apical side is contoured at 4.0σ. e The Zn2+-ascorbate-binding cavity on the apical surface is shown