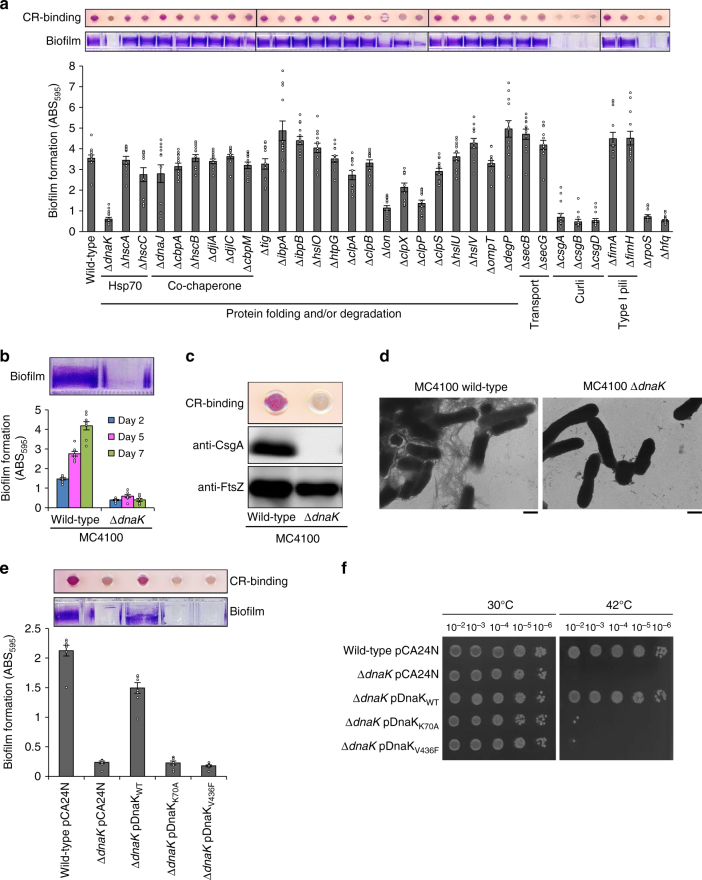
Fig. 1.
DnaK is important for curli-dependent biofilm formation. a Curli production in indicated E. coli strains (Keio collection) was analysed with the CR-binding assay (upper panel). Biofilms formed in a 96-well polystyrene plate were stained with crystal violet (middle panel). The bottom graph shows the quantification of biofilm biomass. b Biofilm formation of other strains. The upper panel shows 7 days biofilms; biomasses were quantified after 2, 5, and 7 days of incubation. c Curli production by indicated E. coli strains was analysed with the CR-binding assay and immunoblotting using anti-CsgA antibody. Curli fibrils were depolymerized to CsgA monomers by applying hexafluoroisopropanol. FtsZ was detected as a loading control. d Extracellular structures of indicated E. coli strains were analysed by transmission electron microscopy. Scales, 500 nm. e Curli production and biofilm formation of the indicated strains were analysed with CR-binding assay and by crystal violet staining. f Complementation assay for evaluating the recovery of the growth defect at high temperature in ΔdnaK. Experiments were repeated at least three times. Means with standard errors and data plots are shown. Full-size scans of immunoblots are shown in Supplementary Fig. 2