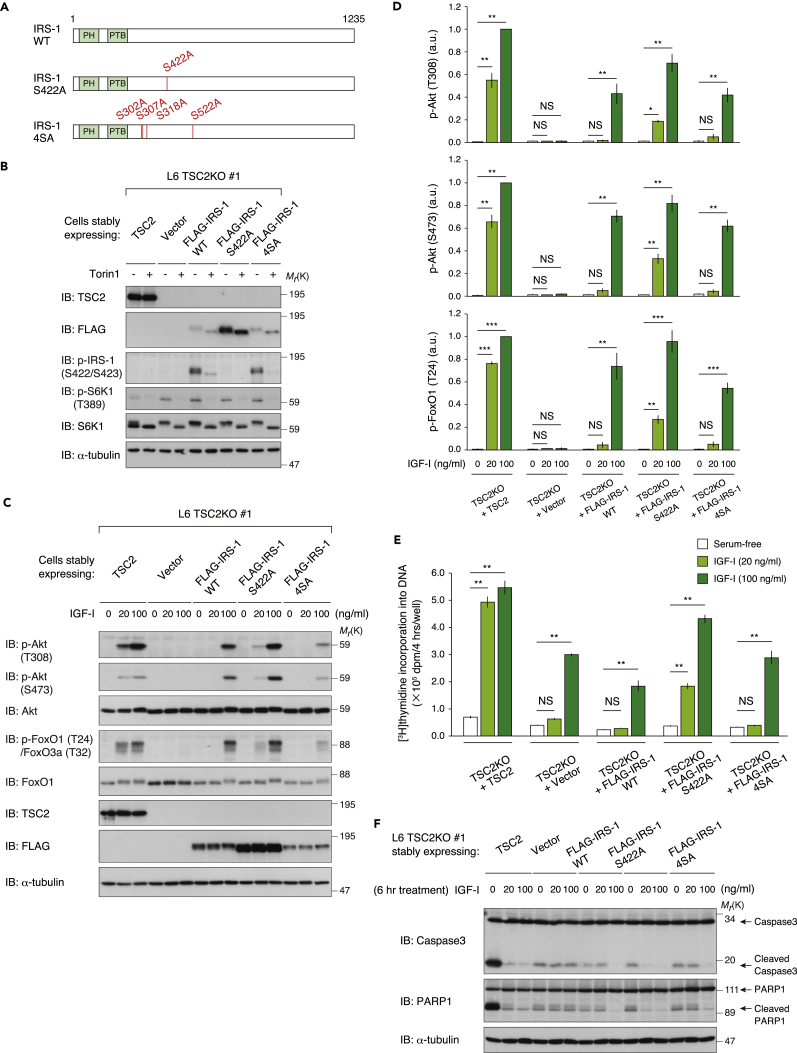
Figure 6.
Expression of IRS-1 S422A Mutant Restores IGF-I Sensitivity in Cells Lacking TSC2
(A) Schematic illustration of wild-type (WT) IRS-1, IRS-1 S422A, and 4SA mutants.
(B) Immunoblot (IB) analysis of whole-cell lysates derived from L6 TSC2 KO cells stably expressing TSC2, FLAG-IRS-1 WT, S422A, 4SA, or empty vector that were serum starved and then collected at 1 hr following Torin1 stimulation.
(C and D) Immunoblot analysis of whole-cell lysates derived from L6 TSC2 KO cells stably expressing TSC2, FLAG-IRS-1 WT, S422A, 4SA, or empty vector that were serum starved and then collected at 5 min following IGF-I stimulation at the indicated concentration (C). Immunoblots of Akt and FoxO1/3a phosphorylation for (C) were quantified, and the graph is shown as mean ± SEM of four independent experiments (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001) (D).
(E) Effects of expression of TSC2 or IRS-1 mutants on IGF-I-induced DNA synthesis in L6 TSC2 KO cells. L6 TSC2 KO cells stably expressing TSC2, FLAG-IRS-1 WT, S422A, 4SA, or empty vector were serum starved and then treated with IGF-I at the indicated concentration for 12 hr. [3H]Thymidine incorporation into DNA during 8–12 hr of IGF-I stimulation was measured. The graph is shown as mean ± SEM (n = 4; **p < 0.01).
(F) L6 TSC2 KO cells stably expressing TSC2, FLAG-IRS-1 WT, S422A, 4SA, or empty vector were placed in serum-free medium with or without IGF-I at the indicated concentration for 6 hr. The collected cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. See also Figure S6A.
The data shown are representative of at least three independent experiments. See also Figure S6.