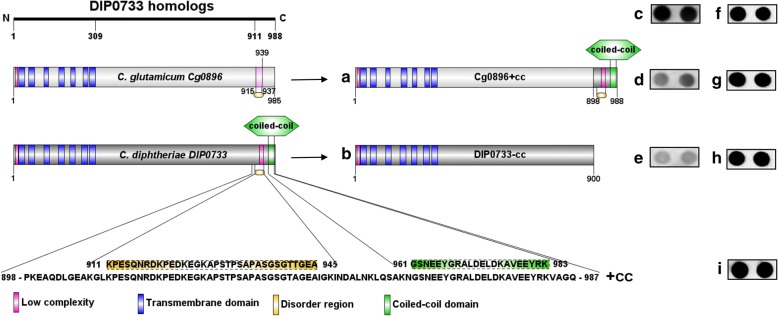
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of DIP0733 homologs and their truncated forms. Left: DIP0733 homologs in non-pathogenic (C. glutamicum) and pathogenic (C. diphtheriae) corynebacteria and their common features: low complexity regions (pink boxes), transmembrane helix domains (blue boxes), disorder regions (yellow boxes) and coiled-coil domain (green boxes). Right: strategy for the cloning of the truncated DIP0733 variants into pXMJ19. The C. glutamicum DIP0733 homolog sequence with the fused coding sequence for the coiled-coil domain from C. diphtheriae is represented by Cg0896 + cc (a). DIP0733 homolog sequence from C. diphtheriae without the coiled-coil domain and disorder region are represented by DIP0733-cc (b). Similar transcription levels of the DIP0733 homologs (Cg0896, Cg0896 + cc, DIP0733-cc) are demonstrated by RNA hybridization with the respective probes for DIP0733 homologs (c-e) and 16SrRNA respectively (f-h). The transcription levels of the control strains transformed with the empty plasmid was detected for 16SrRNA probe (i) and no signal for DIP0733 homolog probes was observed (data not shown)