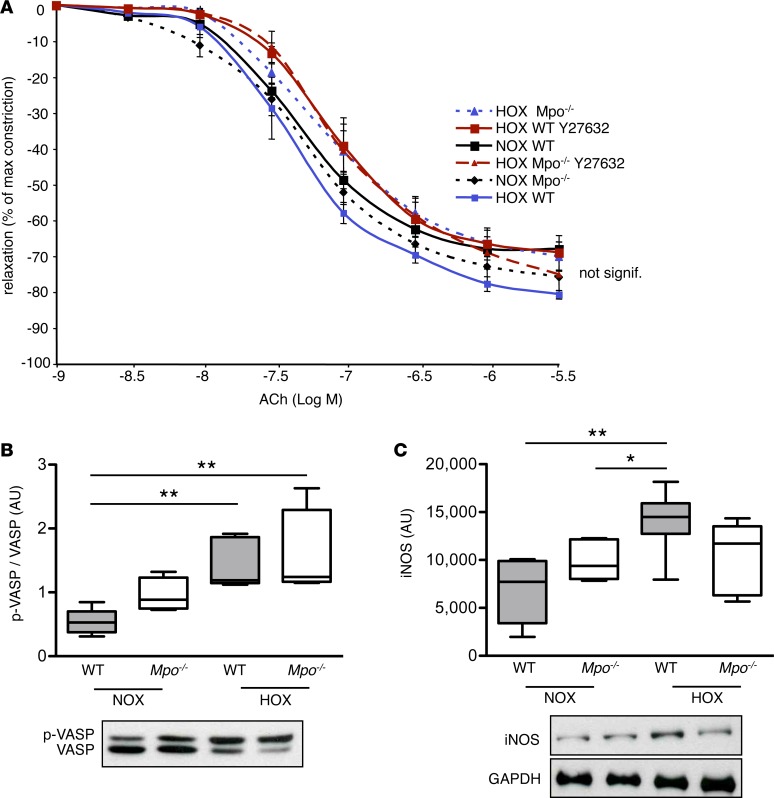
Figure 3. Pulmonary nitric oxide bioavailability.
Pulmonary artery nitric oxide (NO) bioavailability is not affected in Mpo–/– mice upon hypoxia (HOX). (A) Mice were maintained for 28 days under normoxia (NOX) or HOX (10% O2), and the Rho-kinase inhibitor Y-27632 was administered 1 hour prior to sacrifice. Relaxation of explanted pulmonary arteries in response to acetylcholine (ACh) was assessed by isometric force measurements and expressed as % of maximal prostaglandin F2α-mediated constriction with mean ± SEM. n = 5 (WT NOX), 6 (Mpo–/– NOX), 4 (WT HOX), 5 (Mpo–/– HOX), 7 (WT Y27632), 6 (Mpo–/– Y27632). Statistical analysis was performed by 1-way ANOVA for repeated measures. Differences are not statistically significant. (B) Lung homogenates of mice after 28 days of NOX or HOX were analyzed by Western blot, and protein amount of phosphorylated vasodilator stimulated phosphoprotein (p-VASP, Ser-157) in relation to dephosphorylated VASP was assessed. n = 5 (WT NOX), 4 (Mpo–/– NOX), 5 (WT HOX), 4 (Mpo–/– HOX); **P < 0.01. (C) Protein amount of inducible NO-synthase (iNOS) related to GAPDH was assessed in lung homogenates of mice after 28 days of NOX or HOX. n = 5 (WT NOX), 5 (Mpo–/– NOX), 6 (WT HOX), 5 (Mpo–/– HOX); *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. Data in B and C represent median with interquartile range; whiskers indicate minimum to maximum. Statistical analysis was performed with 1-way ANOVA with LSD post hoc test.