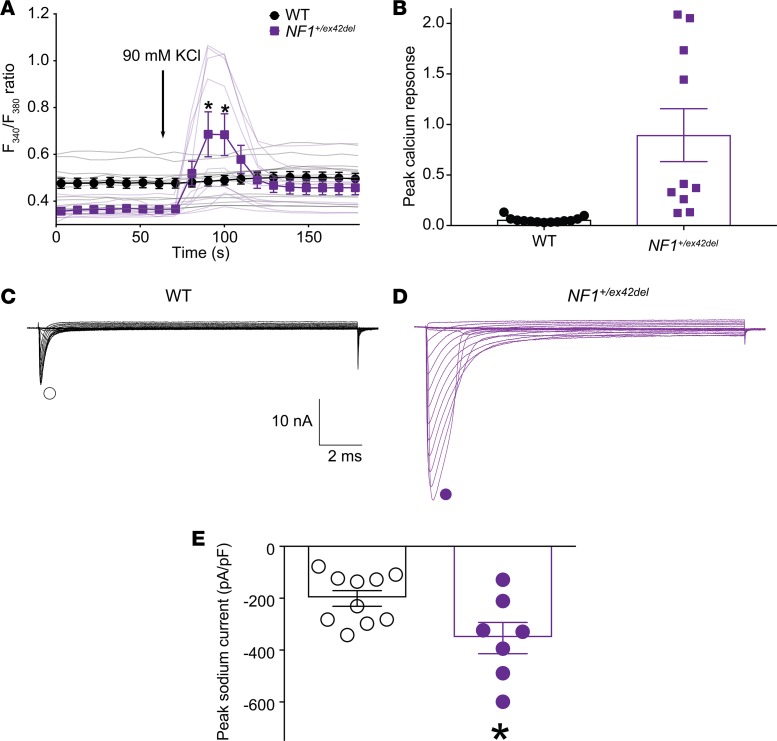
Figure 8. DRGs from mutant NF1+/ex42del pigs have increased N-type calcium activity and sodium currents compared with WT animals.
Individual calcium responses and summary data of DRG neurons challenged with 90 potassium chloride [(n = 13 for WT (4-month old female pig) and n = 10 for NF1+/ex42del (4-month old male swine)] (A). Peak calcium responses are plotted in B. Asterisks indicate statistical significance compared with untreated cells (*P < 0.05, Two-tailed Student’s t test analyses). Representative family of total Na+ current traces are illustrated for sensory neurons from WT or NF1+/ex42del swine (C). Peak current densities for the indicated conditions (D). Numbers of cells: [(n = 13 for WT (4-month old female swine) and n = 10 for NF1+/ex42del (4-month old male swine)]. Asterisk denotes statistical significance compared with WT cells (Mean ± SEM, *P < 0.05, Unpaired 2-tailed Student’s t test). Experiment was performed with experimenter blinded to the genotype.