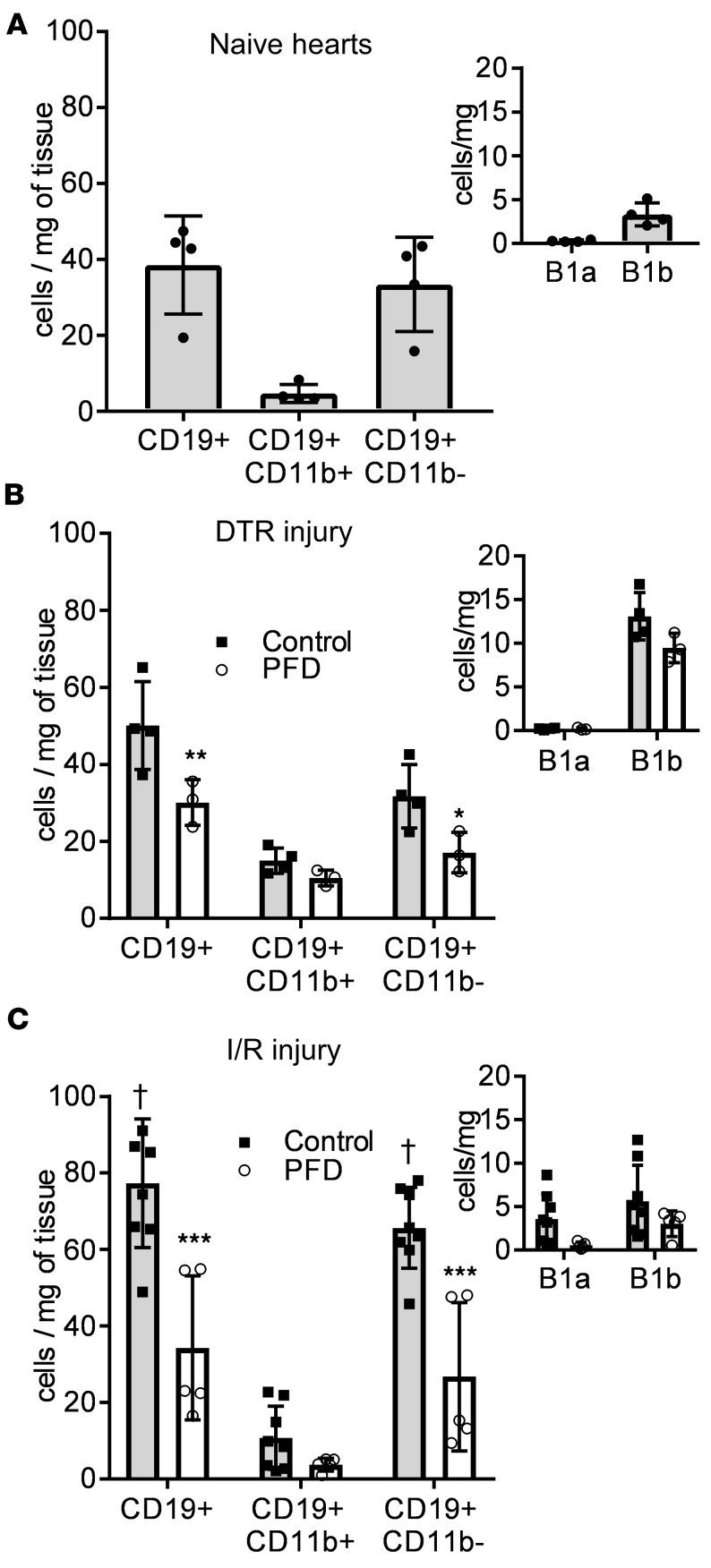
Figure 5. Characterization of subsets of myocardial B lymphocytes at baseline and after DT-induced injury and I/R injury.
(A) Analysis of subsets of myocardial CD19+ B lymphocytes in naive hearts (n = 4). (B) Mice expressing the diphtheria toxin receptor (DTR) in the myocardium were exposed to diphtheria toxin (DT) and fed either regular chow (control, gray bars) or chow enriched with pirfenidone (PFD, white bars). Mice were sacrificed at day 4 after DT injection and the heart was collected for analysis of myocardial CD19+ B lymphocytes via flow cytometry (n = 4 control, n = 3 pirfenidone). (C) Wild-type mice were subjected to 90 minutes closed-chest ischemia followed by reperfusion (I/R injury). Mice were fed either regular chow (control, gray bars) or chow enriched with pirfenidone (PFD, white bars). Mice were sacrificed at day 4 after I/R injury and the heart was collected for analysis of myocardial CD19+ B lymphocytes via flow cytometry (n = 8 controls, n = 5 pirfenidone). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 versus control; †P < 0.001 versus naive hearts. Bars represent the mean, and error bars represent standard deviation. P values were calculated with 2-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test for multiple comparisons.