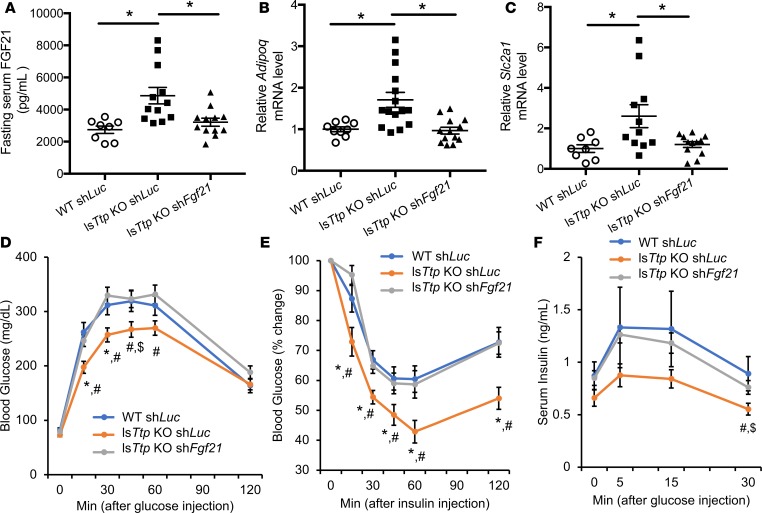
Figure 7. Increased liver-derived circulating FGF21 is responsible for improved systemic diabetic parameters after high-fat diet in the setting of hepatic Ttp deletion.
(A) Fasting levels of circulating FGF21 are effectively reduced in lsTtp-KO mice injected with a hepatotropic Fgf21 shRNA AAV8 virus (shFgf21) at 3 weeks of age and then fed HFD for 12 weeks. (B and C) Downregulation of Fgf21 in lsTtp-KO mice leads to normalization of Adipoq mRNA levels in adipose tissue (B) and Slc2a1 mRNA levels in skeletal muscle (C) after HFD; n = 8 for WT shLuc and 12 for lsTtp-KO shLuc and shFgf21. *P < 0.05 by 1-way ANOVA with post hoc Fisher’s LSD test. (D–F) lsTtp-KO mice injected with Fgf21 shRNA AAV8 have reversal of glucose tolerance (D), insulin sensitivity (E), and glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (F) after HFD compared with lsTtp-KO mice injected with shLuc (n = 7 for WT shLuc, 9 for lsTtp-KO shLuc, and 16 for lsTtp-KO shFgf21 for D–F) #P < 0.05 between lsTtp-KO shFgf21 and lsTtp-KO shLuc, *P < 0.05 between lsTtp-KO shLuc and WT shLuc, $P < 0.1 between lsTtp-KO shLuc and WT shLuc. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, using 1-way ANOVA with post hoc Fisher’s LSD test.