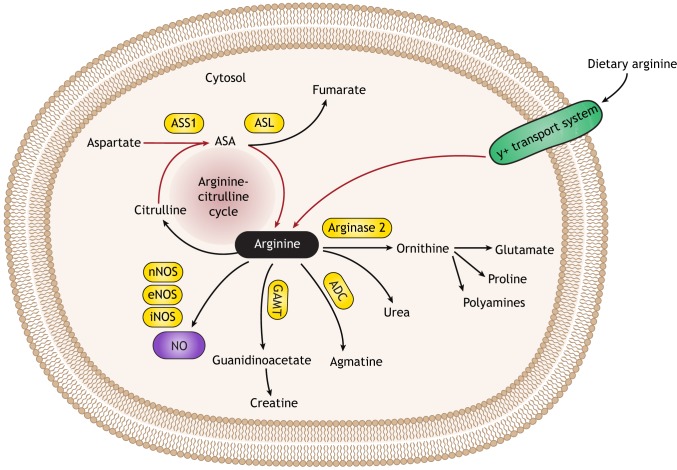
Fig. 1.
A schematic illustration of arginine metabolism outside of the liver. Arginine from dietary intake can enter a cell via the y+ transport system or it can be synthesized endogenously by the arginine-citrulline cycle (red arrows). In contrast to the single enzyme that synthesizes arginine (ASL), many enzymes utilize arginine as their substrate (black arrows), to synthesize a range of compounds, including ornithine, agmatine, guanidinoacetate and NO, in accordance with cellular needs. NO is synthesized from arginine by either one or by all three NOS isoforms (eNOS, iNOS or nNOS), depending on cellular context. ADC, arginine decarboxylase; ASA, argininosuccinic acid; ASL, argininosuccinate lyase; ASS, argininosuccinate synthase 1; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; GAMT, guanidinoacetate methyltransferase; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; NO, nitric oxide; nNOS, neuronal nitric oxide synthase.