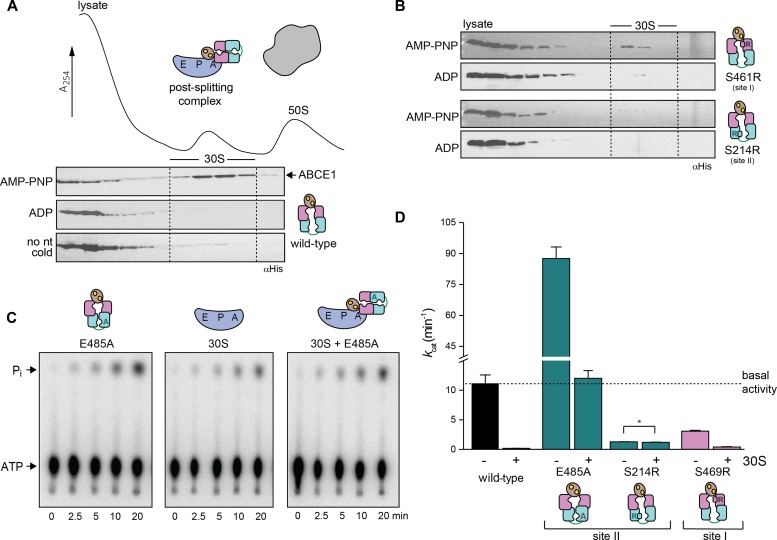
Figure 5. Post-SC requires closure of site II and inhibits the ATPase activity of ABCE1.
(A) The post-SC is assembled from S. solfataricus cell lysate (contains only 30S and 50S subunits) and recombinant ABCE1. WT protein essentially requires high temperature and AMP-PNP for 30S binding. (B) Blockage of site II by the S214R mutation severely inhibits post-SC formation. (C) 30S binding inhibits the ATPase activity of ABCE1E485A (1 μM), as demonstrated by TLC of 32P-γ-ATP (2 mM). ATP hydrolysis drops to the level of background 30S activity if the small subunit is added to the hyperactive E485A variant. (D) ATPase activity of ABCE1 is inhibited if a post-SC is efficiently formed. Strikingly, ATP hydrolysis rate of ABCE1S214R does not change upon addition of 30S (*) because the S214R mutation prevents 30S binding. The overall drop of kcat for ABCE1 in this experiment results from the higher Mg2+ (20 mM) concentration used for 30S binding compared with 2.5 mM Mg2+ in the ATPase measurements with ABCE1 only. Representative set of three independent experiments.