Figure 1.
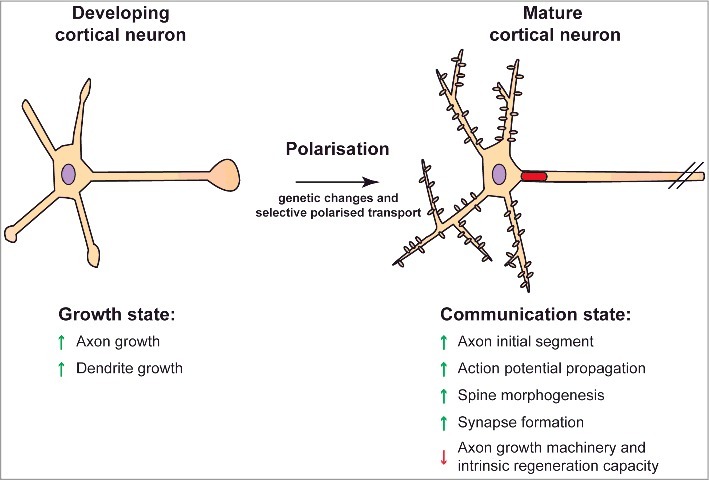
Polarisation of cultured cortical neurons. Neurons undergo various developmental stages during polarisation. Genetic changes and selective transport of proteins contribute to neuronal polarisation. For simplification purposes, two developmental stages are categorized here. Developing cortical neurons exist in a growth state that promotes first axonal and then dendritic outgrowth. As neurons mature, there is a decline in their growth capacity as they become geared for neurotransmission. The neurons form an axon initial segment that propagates the action potential and also contributes to polarised membrane protein transport. Mature cortical neurons have a poor intrinsic capacity for axon regeneration.
