Figure 2.
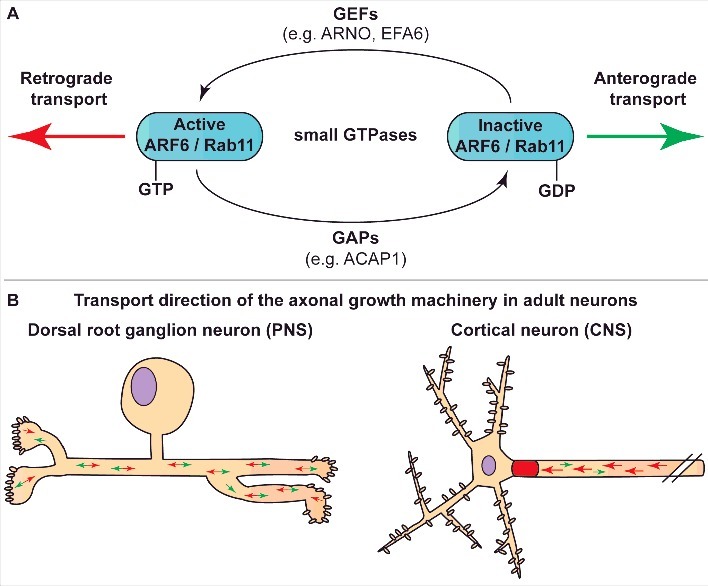
The activation state of small GTPases ARF6 and Rab11 regulate the transport direction of the axonal growth machinery. A. Molecular mechanisms of GTPases activation and inactivation. Active, GTP-bound ARF6 / Rab11 stimulate retrograde transport via dyneins, whilst GDP bound ARF6 / Rab11 favours anterograde transport via kinesin motors. Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs), such as ARNO and EFA6, activate GTPases by exchanging GDP for GTP and thereby promote retrograde transport. GTPase-activating proteins (GAPs), including ACAP1, stimulate GTP to GDP hydrolysis and promote anterograde transport of kinesins. B. Summary of the transport direction of the axonal growth machinery in adult dorsal root ganglion (DRG) and cortical neurons. Vesicles containing integrins move in bi-directional direction in DRG, while cortical neurons exhibit predominant retrograde transport of axonal growth machinery away from the axon. Green arrow indicates anterograde transport, red arrow indicates retrograde transport. PNS, peripheral nervous system; CNS, central nervous system.
