Figure 1.
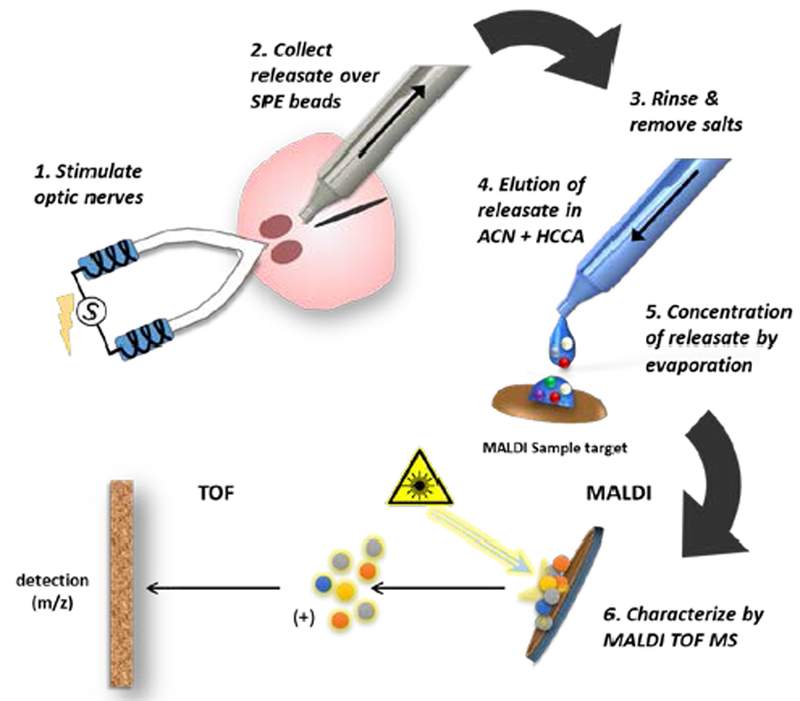
Schematic of the workflow for neuropeptide collection from the SCN brain slice and MS analysis. 1. The optic nerves (ON) attached to a horizontal SCN brain slice are stimulated in tandem by suction electrodes or the SCN is treated directly by droplet containing a chemical stimulus. 2. Releasate is aspirated through a micropipette containing solid-phase extraction beads (SPEs), which bind peptides based on their charge. 3. The beads are rinsed to remove salts and then samples (represented as small colored circles) are transferred to a MALDI target surface. 4. Bound analytes are eluted with acetonitrile (ACN) and addition of a cyano-4 hydroxycinnamic acid (HCCA) MALDI matrix solution. 5. As the acetonitrile evaporates, analytes are concentrated with MALDI matrix onto discrete hydrophobic regions within the HCCA crystals on the pre-treated target plate. 6. The sample is volatized and ionized by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI). Following ionization, the analytes are subjected to a mass analyzer and detector for spectrophotometric analysis where their mass/charge ratio (m/z) is determined.
